RPC Operation Interface
All RPC operations are data-driven within the server, using the YANG rpc statement for the operation and SIL callback functions.
Any new protocol operation can be added by defining a new YANG rpc statement in a module, and providing the proper SIL code.
RPC Callbacks
For the Global version of RPC callbacks, see Global RPC Callback.
RPC Callback Template
The 'agt_rpc_method_t' typedef in agt/agt_rpc.h is used as the
callback template for all RPC callback phases.
-
typedef status_t (*agt_rpc_method_t)(ses_cb_t *scb, rpc_msg_t *msg, xml_node_t *methnode)
Template for RPC server callbacks.
The same template is used for all RPC callback phases The callback is expected to validate if needed and then invoke if needed.
- Param scb:
session invoking the RPC
- Param msg:
message in progress for this <rpc> request
the msg->rpc_input value node contains the input (if any). It is a container matching the rpc/input node for the YANG rpc
- Param methnode:
XML node for the operation, which can be used in error reporting (or ignored)
- Return:
return status for the phase
An error in validate phase will cancel invoke phase
An rpc-error will be added if an error is returned and the msg error Q is empty
RPC Callback Initialization
The 'agt_rpc_register_method' function in agt/agt_rpc.h is used
to provide a callback function for a specific callback phase. The same
function can be used for multiple phases if desired.
This function call is usually generated automatically in the SIL or SIL-SA code stubs.
-
status_t agt_rpc_register_method(const xmlChar *module, const xmlChar *method_name, agt_rpc_phase_t phase, agt_rpc_method_t method)
Example Registration Code:
res = agt_rpc_register_method(
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_make_toast,
AGT_RPC_PH_VALIDATE,
y_toaster_make_toast_validate);
if (res != NO_ERR) {
return res;
}
RPC Callback Cleanup
The 'agt_rpc_unregister_method' function in agt/agt_rpc.h is used
to remove a callback function for all callback phases.
Warning
This function must be called once if any callback phase was registered. Memory may not be properly freed if an RPC callback is not properly unregistered.
This function call is usually generated automatically in the SIL or SIL-SA code stubs.
-
void agt_rpc_unregister_method(const xmlChar *module, const xmlChar *method_name)
Example Unregistration Code:
agt_rpc_unregister_method(
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_make_toast);
Force an RPC Operation to be Unsupported
It is possible for the SIL instrumentation to turn support for an RPC operation off in the server.
If this API is used then the RPC operation will be removed from the list of operations that can be used in the server.
-
void agt_rpc_unsupport_method(const xmlChar *module, const xmlChar *method_name)
mark an RPC method or action as unsupported within the server
this is needed for operations dependent on capabilities
- Parameters:
module -- module name of RPC method (really module name)
method_name -- RPC method name
Use this function with care. It may break the server if this API is used on a server-provided RPC operation.
Example Usage:
agt_rpc_unsupport_method(
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_make_toast);
RPC Message Header
The NETCONF server will parse the incoming XML message and construct an RPC message header, which is used to maintain state and any other message-specific data during the processing of an incoming <rpc> request.
rpc_msg_t
The 'rpc_msg_t' data structure defined in ncx/rpc.h
is used to represent an RPC operation.
It is a high-level control block which contains a low-level 'xml_msg_hdr_t'
struct within it.
-
struct rpc_msg_t
NETCONF Server and Client RPC Request/Reply Message Header.
Public Members
-
dlq_hdr_t qhdr
Queue header to store RPC messages in a queue (within the session header)
-
xml_msg_hdr_t mhdr
generic XML message header Most in-message state is kept in the mhdr There are several places in the code where the mhdr is used alone so there is no coupling to the RPC layer.
Contains XML message prefix map and other data used to parse the request and generate the reply.
-
xml_attrs_t *rpc_in_attrs
incoming: top-level rpc element data Queue of xml_attr_t representing any XML attributes that were present in the <rpc> element.
A callback function may add xml_attr_t structs to this queue to send in the reply.
-
struct obj_template_t_ *rpc_method
incoming: Back-pointer to the object template for this RPC operation.
2nd-level method name element data, used in agt_output_filter to check get or get-config; cannot import obj.h here! The object template type will be OBJ_TYP_RPC for an RPC method For an action this will be the top-level <action> RPC wrapper in the YANG namespace
-
int rpc_agt_state
incoming: SERVER RPC processing state Enum value (0, 1, 2) for the current RPC callback phase.
-
op_errop_t rpc_err_option
Enum value for the <error-option> parameter.
This is only set if an edit operation is in progress.
-
op_editop_t rpc_top_editop
Enum value for the <default-operation> parameter.
This is only set if an edit operation is in progress.
-
val_value_t *rpc_input
Value tree representing the container of 'input' parameters for this RPC operation.
For an action, the rpc_input node is not used. Instead the rpc_actionval backptr is used instead. This is malloced in rpc_new_msg but not filled in.
-
struct sil_sa_cb_t_ *rpc_sil_sa_cb
backptr to SIL-SA edit control block if WITH_YCONTROL=1
-
dlq_hdr_t rpc_inputQ
the rpc_inputQ is used with JSON encoded input since an array is allowed at the top-level; it is used instead of rpc_input if encoding == JSON, even if only 1 array node is parsed;
Q of val_value_t *
-
void *rpc_user1
Void pointer that can be used by method routines to save context or whatever to store SIL-specific data.
This pointer is preserved, transferred from validate to invoke so data does not need to be regenerated or retrieved
-
void *rpc_user2
Same use as rpc_user1.
-
uint32 rpc_returncode
Internal return code used to control nested callbacks.
-
rpc_data_t rpc_data_type
incoming: get method reply handling builtin For RPC operations that return data, this enumeration MUST be set to indicate which type of data is returned.
RPC_DATA_STD: A <data> container will be used to encapsulate any returned data, within the <rpc-reply> element.
RPC_DATA_YANG: The <rpc-reply> element will be the only container encapsulated any returned data. If the rpc_datacb is non-NULL then it will be used as a callback to generate the rpc-reply inline, instead of buffering the output. The rpc_data and rpc_filter parameters are optionally used by the rpc_datacb function to generate a reply.
-
void *rpc_datacb
For operations that return streamed data, this pointer is set to the desired callback function to use for generated the data portion of the <rpc-reply> XML response.
The template for this callback is agt_rpc_data_cb_t, found in agt_rpc.h
-
dlq_hdr_t rpc_dataQ
For operations that return stored data, this queue of val_value_t structures can be used to provide the response data.
Each val_value_t structure will be encoded as one of the corresponding RPC output parameters. The data will be returned in order. The val_value_t nodes will be freed when the rpc_msg_t is freed
-
op_filter_t rpc_filter
Internal structure for optimizing subtree and XPath retrieval operations.
backptrs for get* methods.
-
struct agt_cfg_transaction_t_ *rpc_txcb
incoming: agent database edit transaction control block must be freed by an upper layer if set to malloced data
-
boolean rpc_parse_errors
load-config parse-error and —startup-error=continue flag if the val_purge_errors_from_root function is needed
-
xmlChar *rpc_message_id
debugging and audit message string.
Contains the message-id attribute found in the <rpc> header. backptr into rpc_in_attrs.
-
xmlChar *rpc_trace_id
debugging and audit message string.
Contains the trace-id attribute found in the <rpc> header. backptr into rpc_in_attrs.
-
boolean rpc_replay_config
TRUE if this RPC is being called in replay config mode.
-
boolean rpc_with_template
—with-template parameter was seen in the validate phase
-
dlq_hdr_t hook_inputQ
points to add_edit_value node comming from the users freed in the end of transaction.
Used only with set-hook. Contains Q of val_value_t.
-
boolean rpc_defer_reply
YPSERVER mode is skipping the regular rpc-reply phase and will send the reply after doing the remote task.
-
xml_attrs_t rpc_defer_in_attrs
the top->attrs gets deleted so a deferred rpc-reply needs to save the rpc_in_attrs.
This is malloced and cleaned when rpc-msg_t is freed
-
rpc_rpytyp_t rpc_reply_type
saved reply type needed for audit record
-
time_t rpc_start_time
saved timestamp when started for audit record
-
const xmlChar *subrpc_filespec
saved by agt_db_api.c so the ycontrol callback function can generate an external value with the DB-API subrpc response message
-
boolean rpc_in_delete_children_first
set to TRUE for a EDIT2 SIL callback when a nested child node is being deleted because of sil-delete-children-first
-
dlq_hdr_t qhdr
RPC Validate Callback Function
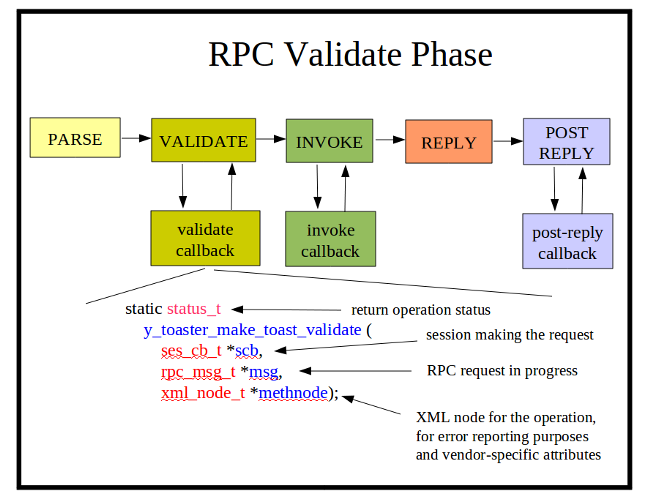
The RPC validate callback function is optional to use. Its purpose is to validate any aspects of an RPC operation, beyond the constraints checked by the server engine. Only 1 validate function can register for each YANG rpc statement. The standard NETCONF operations are reserved by the server engine. There is usually zero or one of these callback functions for every 'rpc' statement in the YANG module associated with the SIL code.
It is enabled with the agt_rpc_register_method function, within the phase 1 initialization callback function.
The yangdump-sdk code generator will create this SIL callback function by default. There will be C comments in the code to indicate where your additional C code should be added.
The val_find_child (or val_child_find) function is commonly used to find particular parameters within the RPC input section, which is encoded as a val_value_t tree.
The agt_record_error function is commonly used to record any parameter or other errors. In the libtoaster example, there are internal state variables ("toaster_enabled" and "toaster_toasting"), maintained by the SIL code, which are checked in addition to any provided parameters.
Example RPC YANG definition:
rpc make-toast {
description
"Make some toast.
The toastDone notification will be sent when
the toast is finished.
An 'in-use' error will be returned if toast
is already being made.
A 'resource-denied' error will be returned
if the toaster service is disabled.";
input {
leaf toasterDoneness {
type uint32 {
range "1 .. 10";
}
default 5;
description
"This variable controls how well-done is the
ensuing toast. It should be on a scale of 1 to 10.
Toast made at 10 generally is considered unfit
for human consumption; toast made at 1 is warmed
lightly.";
}
leaf toasterToastType {
type identityref {
base toast:toast-type;
}
default toast:wheat-bread;
description
"This variable informs the toaster of the type of
material that is being toasted. The toaster
uses this information, combined with
toasterDoneness, to compute for how
long the material must be toasted to achieve
the required doneness.";
}
}
}
Example SIL Function:
/********************************************************************
* FUNCTION y_toaster_make_toast_validate
*
* RPC validation phase
* All YANG constraints have passed at this point.
* Add description-stmt checks in this function.
*
* INPUTS:
* see agt/agt_rpc.h for details
*
* RETURNS:
* error status
********************************************************************/
static status_t
y_toaster_make_toast_validate (
ses_cb_t *scb,
rpc_msg_t *msg,
xml_node_t *methnode)
{
status_t res;
val_value_t *errorval;
const xmlChar *errorstr;
val_value_t *toasterDoneness_val;
val_value_t *toasterToastType_val;
uint32 toasterDoneness;
val_idref_t *toasterToastType;
res = NO_ERR;
errorval = NULL;
errorstr = NULL;
toasterDoneness_val = val_find_child(
msg->rpc_input,
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_toasterDoneness);
if (toasterDoneness_val != NULL && toasterDoneness_val->res == NO_ERR) {
toasterDoneness = VAL_UINT(toasterDoneness_val);
}
toasterToastType_val = val_find_child(
msg->rpc_input,
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_toasterToastType);
if (toasterToastType_val != NULL && toasterToastType_val->res == NO_ERR) {
toasterToastType = VAL_IDREF(toasterToastType_val);
}
/* added code starts here */
if (toaster_enabled) {
/* toaster service enabled, check if in use */
if (toaster_toasting) {
res = ERR_NCX_IN_USE;
} else {
/* this is where a check on bread inventory would go */
/* this is where a check on toaster HW ready would go */
}
} else {
/* toaster service disabled */
res = ERR_NCX_RESOURCE_DENIED;
}
/* added code ends here */
/* if error: set the res, errorstr, and errorval parms */
if (res != NO_ERR) {
agt_record_error(
scb,
&msg->mhdr,
NCX_LAYER_OPERATION,
res,
methnode,
NCX_NT_STRING,
errorstr,
NCX_NT_VAL,
errorval);
}
return res;
} /* y_toaster_make_toast_validate */
RPC Invoke Callback Function
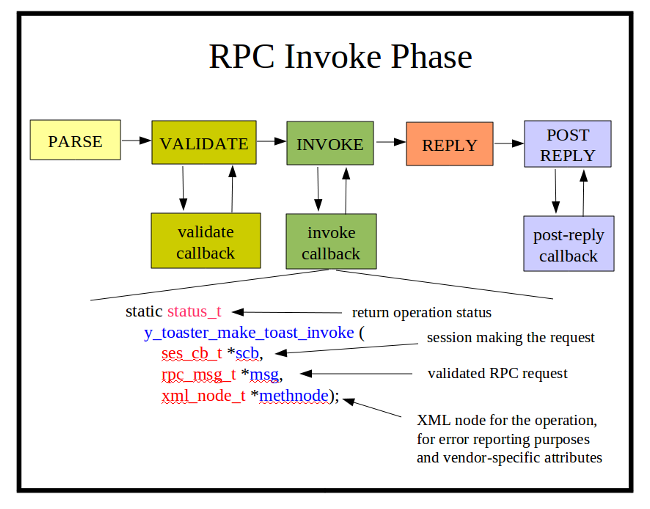
The RPC invoke callback function is used to perform the operation requested by the client session. Only 1 invoke function can register for each YANG rpc statement. The standard NETCONF operations are reserved by the server engine. There is usually one of these callback functions for every 'rpc' statement in the YANG module associated with the SIL code.
The RPC invoke callback function is optional to use, although if no invoke callback is provided, then the operation will have no affect. Normally, this is only the case if the module is be tested by an application developer, using netconfd-pro as a server simulator.
It is enabled with the agt_rpc_register_method function, within the phase 1 initialization callback function.
The yangdump-sdk code generator will create this SIL callback function by default. There will be C comments in the code to indicate where your additional C code should be added.
For RPC operations that return either an <ok> or <rpc-error> response, there is nothing more required of the RPC invoke callback function.
For operations which return some data or <rpc-error>, the SIL code must do 1 of 2 additional tasks:
add a val_value_t structure to the 'rpc_dataQ' queue in the rpc_msg_t for each parameter listed in the YANG rpc 'output' section.
set the 'rpc_datacb' pointer in the rpc_msg_t structure to the address of your data reply callback function.
Example RPC Invoke SIL Function Registration
res = agt_rpc_register_method(
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_make_toast,
AGT_RPC_PH_INVOKE,
y_toaster_make_toast_invoke);
if (res != NO_ERR) {
return res;
}
Example RPC Invoke SIL Function
/********************************************************************
* FUNCTION y_toaster_make_toast_invoke
*
* RPC invocation phase
* All constraints have passed at this point.
* Call device instrumentation code in this function.
*
* INPUTS:
* see agt/agt_rpc.h for details
*
* RETURNS:
* error status
********************************************************************/
static status_t
y_toaster_make_toast_invoke (
ses_cb_t *scb,
rpc_msg_t *msg,
xml_node_t *methnode)
{
status_t res;
val_value_t *toasterDoneness_val;
val_value_t *toasterToastType_val;
uint32 toasterDoneness;
val_idref_t *toasterToastType;
res = NO_ERR;
toasterDoneness = 0;
toasterDoneness_val = val_find_child(
msg->rpc_input,
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_toasterDoneness);
if (toasterDoneness_val != NULL && toasterDoneness_val->res == NO_ERR) {
toasterDoneness = VAL_UINT(toasterDoneness_val);
}
toasterToastType_val = val_find_child(
msg->rpc_input,
y_toaster_M_toaster,
y_toaster_N_toasterToastType);
if (toasterToastType_val != NULL && toasterToastType_val->res == NO_ERR) {
toasterToastType = VAL_IDREF(toasterToastType_val);
}
/* invoke your device instrumentation code here */
/* make sure the toasterDoneness value is set */
if (toasterDoneness_val == NULL) {
toasterDoneness = 5; /* set the default */
}
/* arbitrary formula to convert toaster doneness to the
* number of seconds the toaster should be on
*/
toaster_duration = toasterDoneness * 12;
/* this is where the code would go to adjust the duration
* based on the bread type
*/
if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\ntoaster: starting toaster for %u seconds",
toaster_duration);
}
/* this is where the code would go to start the toaster
* heater element
*/
/* start a timer to toast for the specified time interval */
res = agt_timer_create(toaster_duration,
FALSE,
toaster_timer_fn,
NULL,
&toaster_timer_id);
if (res == NO_ERR) {
toaster_toasting = TRUE;
} else {
agt_record_error(
scb,
&msg->mhdr,
NCX_LAYER_OPERATION,
res,
methnode,
NCX_NT_NONE,
NULL,
NCX_NT_NONE,
NULL);
}
/* added code ends here */
return res;
} /* y_toaster_make_toast_invoke */
Example RPC Invoke Callback
This example demonstrates some API functions that are available to an RPC or YANG action callback function.
Example YANG Modele
module deluser {
namespace "urn:vendor:yumaworks:deluser";
prefix delu;
revision 2024-02-02;
rpc delete-user {
description "Remove the user from the system";
input {
leaf user-name {
type string {
length "1..max";
}
mandatory true;
}
}
}
}
The 'delete-user' invoke callback function calls a static function 'do_delete_user' to perform the following:
read the '/nacm/groups' configuration data
traverse each 'group' child entry found
search for the specified 'user-name'
if found, add the user-name to the YANG Patch edit list
if any edits, apply the YANG Patch to the server
Example YANG Data
The server has the following NACM groups: 'G1', 'G2', and 'G3'.
The user-name 'U1' is being deleted by the client
> delete-user user-name=U1
Example Invoke Callback Function
If the code is generated from 'yangdump-pro' then the file 'u_deluser.c' will contain the function 'u_delu_delete_user_invoke'.
/**
* @brief Invocation phase callback for "<delete-user>" operation. (agt_rpc_method_t)
*
* Validation callback has passed at this point.
* Call device instrumentation code in this function.
*
* @param scb session invoking the RPC operation.
* @param msg message in progress for this <rpc> request.
* The msg->rpc_input value node contains the input (if any).
* It is a container matching the rpc/input node for the YANG rpc.
* @param methnode XML node for the operation, which can be used
* in error reporting (or ignored).
* @return return status for the phase.
* - An error in validate phase will cancel invoke phase
* - An rpc-error will be added if an error is returned and
* the msg error Q is empty
*/
status_t u_delu_delete_user_invoke (
ses_cb_t *scb,
rpc_msg_t *msg,
xml_node_t *methnode)
{
status_t res = NO_ERR;
if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\nStart SIL invoke rpc <delete-user> from module deluser");
}
val_value_t *errorval = NULL;
val_value_t *inputval = agt_get_rpc_input(msg);
if (inputval == NULL) return ERR_NCX_OPERATION_FAILED;
val_value_t *v_user_name_val = NULL;
const xmlChar *v_user_name = NULL;
/* RPC Input: user-name */
v_user_name_val = val_find_child(
inputval,
y_delu_M_delu,
y_delu_N_user_name);
if (v_user_name_val) {
v_user_name = VAL_STRING(v_user_name_val);
errorval = v_user_name_val;
} else {
res = ERR_NCX_MISSING_PARM;
}
/* invoke your device instrumentation code here */
res = do_delete_user(scb, v_user_name);
if (res != NO_ERR) {
agt_record_error(
scb,
&msg->mhdr,
NCX_LAYER_OPERATION,
res,
methnode,
(errorval) ? NCX_NT_VAL : NCX_NT_NONE,
errorval,
(errorval) ? NCX_NT_VAL : NCX_NT_NONE,
errorval);
}
/* No output nodes expected */
return res;
} /* u_delu_delete_user_invoke */
Example do_delete_user Function
The function 'do_delete_user' is invoked from the callback function. This function does all the work and is not coupled to the RPC callback API.
/**
* @brief Delete a user from NACM
*
* @param scb session invoking the RPC operation.
* @return return status for the phase.
*/
static status_t
do_delete_user (ses_cb_t *scb,
const xmlChar *username)
{
status_t res = NO_ERR;
ncx_cfg_t cfg_id = NCX_CFGID_RUNNING;
const xmlChar *defpath = (const xmlChar *)"/nacm/groups";
/* get the parent container of the NACM group entries */
val_value_t *parentval = agt_val_get_data(cfg_id, defpath, &res);
if (parentval == NULL) {
if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\nGet Data for %s failed (%s)",
defpath, get_error_string(res));
}
return res;
}
if (LOGDEBUG4) {
int32 startindent = 0;
log_debug_t lvl = LOG_DEBUG_DEBUG4;
log_debug4("\nGot value for '%s':", defpath);
val_dump_value(parentval, startindent, lvl);
log_debug4_append("\n");
}
/* even though only child is 'group' use val_child_find
* to make sure no siblings added later get checked
*/
const xmlChar *child_modname = val_get_mod_name(parentval);
const xmlChar *child_name = (const xmlChar *)"group";
val_value_t *groupval =
val_child_find(parentval, child_modname, child_name);
if (groupval == NULL) {
if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\nNo NACM groups found");
}
val_free_value(parentval);
return NO_ERR;
}
/* start a Patch Edit to hold the edits for deleting
* the user-name from each group that it is found
*/
const xmlChar *patch_id_str = (const xmlChar *)"mypatch-1";
boolean system_edit = false;
/* the skip_sil parameter MUST be true for YumaPro implemented
* SIL code such as /nacm
*/
boolean skip_sil = false;
const xmlChar *comment = (const xmlChar *)"From remove_user RPC";
uint32 edit_count = 0;
agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms_cb =
agt_new_edit_parms(patch_id_str,
system_edit,
skip_sil,
comment);
if (parms_cb == NULL) {
val_free_value(groupval);
return ERR_INTERNAL_MEM;
}
while ((groupval != NULL) && (res == NO_ERR)) {
/* get the key leaf for the group */
val_value_t *name =
val_find_child(groupval,
val_get_mod_name(groupval),
(const xmlChar *)"name");
if (name == NULL) {
res = ERR_NCX_OPERATION_FAILED;
continue;
}
/* get the first user-name value */
val_value_t *userval =
val_find_child(groupval,
val_get_mod_name(groupval),
(const xmlChar *)"user-name");
while ((userval != NULL) && (res == NO_ERR)) {
if (!xml_strcmp(username, VAL_STRING(userval))) {
/* found the user so make an edit */
++edit_count;
res = add_delete_user_edit(parms_cb, userval, edit_count);
userval = NULL; // done with this loop either way
continue;
}
userval = val_child_next_same(userval);
}
groupval = val_child_next_same(groupval);
}
/* apply the patch if OK */
if (res == NO_ERR) {
if (edit_count > 0) {
res = agt_apply_patch_edit(scb, parms_cb);
if (res != NO_ERR) {
if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\nApply patch failed (%s)",
get_error_string(res));
}
}
} else if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\nUser '%s' not found in any NACM group",
username);
}
}
val_free_value(groupval);
agt_free_edit_parms(parms_cb);
return res;
} /* do_delete_user */
Key API Functions Used:
The 'agt_val_get_data' function is used to retrieve the NACM configuration data. Refer to the Get Data API section for details.
The 'val_dump_value' function is used to display the NACM data in debug mode. Refer to the Tips For Debugging YANG Instrumentation for details.
The val_child_find function is used to traverse the NACM data looking for the specified 'user-name'.
The val_child_next_same function is used to continue a loop through all the leaf-list instances, searching for the 'user-name' that matches.
Example add_delete_user_edit Function
The function 'add_delete_user_edit' is used to generate the YANG Patch edit for the user-name to delete. It is called from the 'do_delete_user' function.
/**
* @brief Add a delete user edit to the YANG Patch in progress
*
* @param parms_cb Patch control block to use
* @param msg message in progress for this <rpc> request.
* @return return status for the phase.
*/
static status_t
add_delete_user_edit (agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms_cb,
val_value_t *userval,
uint32 edit_num)
{
/* YANG patch internals use old YANG-API format */
ncx_instfmt_t format = NCX_IFMT_YANGAPI;
xmlChar *buff = NULL;
status_t res =
val_gen_instance_id (NULL, userval, format, &buff);
if (res != NO_ERR) {
return res;
}
/* make an edit-id string */
char numbuff[NCX_MAX_NUMLEN+2];
*numbuff = 0;
snprintf(numbuff, NCX_MAX_NUMLEN-1, "E%u", edit_num);
const xmlChar *edit_id_str = (const xmlChar *)numbuff;
const xmlChar *edit_target = buff;
const xmlChar *edit_operation = (const xmlChar *)"delete";
/* these parameters must be NULL for a delete operation */
const xmlChar *edit_xml_value = NULL;
const xmlChar *insert_point = NULL;
const xmlChar *insert_where = NULL;
res = agt_add_patch_edit(parms_cb,
edit_id_str,
edit_target,
edit_operation,
edit_xml_value,
insert_point,
insert_where);
m__free(buff);
return res;
} /* add_delete_user_edit */
Key API Functions Used:
The 'val_gen_instance_id' function is used to generate the path string
for the YANG-API formatted string. Note the NCX_IFMT_YANGAPI
format enumeration used in this special case.
Refer to the Printing the Value Path String from a SIL Edit Callback
section for more details.
The 'agt_add_patch_edit' function is used to add a 'delete' edit request for the 'user-name'. Refer to the Add Edits to Patch Edit Request section for details on this API function.
Example delete-user Invocation
The following log file trace shows the server activity for
ses_accept_input on session 3
ses read OK (221) on session 3
ses: accept buffer ssh/1.1 (221):
#211
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc message-id="4"
xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<delete-user xmlns="urn:vendor:yumaworks:deluser">
<user-name>U1</user-name>
</delete-user>
</rpc>
##
ses_msg: allocate msg 0x55c539d8c640
ses_msg: reused in buff 0x55c539c021f0 for s 3
agt_ses msg ready for session 3
Incoming msg for session 3
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc message-id="4"
xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<delete-user xmlns="urn:vendor:yumaworks:deluser">
<user-name>U1</user-name>
</delete-user>
</rpc>
agt_top: got node
XML node (16:0): START rpc
attr: ns:4 name:xmlns (urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0)
attr: ns:0 name:message-id (4)
agt_top: start dispatch yuma-netconf:rpc
agt_rpc: <delete-user> for 3=andy@127.0.0.1 (m:none) [2024-02-08T23:11:17Z]
XML node (54:1): START delete-user
attr: ns:4 name:xmlns (urn:vendor:yumaworks:deluser)
agt_acm: check <delete-user> RPC allowed for user 'andy'
agt_acm: PERMIT (access-control off)
agt_val_parse: delu:input btyp:container
parse_complex: expecting start-child or end node.
XML node (54:2): START user-name
parse_string: expecting string node.
XML node (0:3): STRING
val(2):U1
parse_string: expecting end for user-name
XML node (54:2): END user-name
parse_complex: expecting start-child or end node.
XML node (54:1): END delete-user
agt_rpc: parse RPC input state
deluser:input {
user-name U1
}
agt_rpc: expecting 'rpc' end node
XML node (16:0): END rpc
add_default: checking 'deluser:input'
add_node_default: checking 'deluser:user-name'
agt_val_rpc_xpathchk: deluser:delete-user start
Checking for leafref backptrs for obj 'user-name'
run_instance_check: deluser:input start
instance_check 'deluser:user-name' against 'deluser:input'
(cnt=1, min=1, max=1)
Start SIL validate rpc <delete-user> from module deluser
Start SIL invoke rpc <delete-user> from module deluser
agt_val: retrieving '/nacm/groups' from running datastore
xpath1: enter value walker for ietf-netconf-acm:nacm (0)
xpath1: enter value walker for ietf-netconf-acm:groups (0)
eval_expr
xpath value result for '/nacm/groups'
typ: nodeset (size: 1) =
node 1 (0x55c539c080a0) VALHDR nacm:groups (1)
Got value for '/nacm/groups':
groups {
group G1 {
name G1
user-name U1
user-name U2
user-name U3
}
group G2 {
name G2
user-name U4
user-name U1
}
group G3 {
name G3
user-name U4
user-name U1
user-name U2
}
}
Converted urlstring (/nacm/groups/group/G1/user-name/U1) to XPath (/nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G1"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"])
.... log details removed
***** start commit phase on running for session 3, transaction 11459 *****
Start full commit of transaction 11459: 3 edits on running config
Start invoking commit SIL callback for delete on ietf-netconf-acm:group
Enter ietf_netconf_acm_nacm_groups_group_edit callback for commit phase
Start key walk for user-name
End key walk for user-name: retkey:
name G1
Clearing user-2-group entries in ACM cache
Finished invoking user callback on ietf-netconf-acm:group
Start invoking commit SIL callback for delete on ietf-netconf-acm:group
Enter ietf_netconf_acm_nacm_groups_group_edit callback for commit phase
Start key walk for user-name
End key walk for user-name: retkey:
name G2
Clearing user-2-group entries in ACM cache
Finished invoking user callback on ietf-netconf-acm:group
Start invoking commit SIL callback for delete on ietf-netconf-acm:group
Enter ietf_netconf_acm_nacm_groups_group_edit callback for commit phase
Start key walk for user-name
End key walk for user-name: retkey:
name G3
Clearing user-2-group entries in ACM cache
Finished invoking user callback on ietf-netconf-acm:group
SIL-SA Commit Complete callbacks OK
edit-transaction 11459: on session 3 by andy@127.0.0.1
time: 2024-02-08T23:11:17Z
message-id: --
trace-id: --
datastore: running
operation: delete
target: /nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G1"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"]
comment: From remove_user RPC
edit-transaction 11459: on session 3 by andy@127.0.0.1
time: 2024-02-08T23:11:17Z
message-id: --
trace-id: --
datastore: running
operation: delete
target: /nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G2"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"]
comment: From remove_user RPC
edit-transaction 11459: on session 3 by andy@127.0.0.1
time: 2024-02-08T23:11:17Z
message-id: --
trace-id: --
datastore: running
operation: delete
target: /nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G3"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"]
comment: From remove_user RPC
Complete commit OK of transaction 11459 on running database
YP-HA: Active: skip update: not enabled
Writing <running> config to file '/home/andy/.yumapro/startup-cfg.xml'
agt_cb: Enter run_startup_hook
agt_ncx: Saving config with temp filename (/home/andy/.yumapro/startup-cfg.xml.temp)
xml_wr: skip xmlns duplicate (9=http://netconfcentral.org/ns/yuma-ncx)
ses: free scb: superuser@none sid: 0 fd: 0
Generating <netconf-config-change> notification
Queing <netconf-config-change> notification for stream NETCONF (cnt: 37)(id: 38)
Event Ancestor Keys: none
Event Payload:
ncn:changed-by {
username andy
session-id 3
source-host 127.0.0.1
}
ncn:datastore running
ncn:edit {
target /nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G1"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"]
operation delete
}
ncn:edit {
target /nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G2"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"]
operation delete
}
ncn:edit {
target /nacm:nacm/nacm:groups/nacm:group[nacm:name="G3"]/nacm:user-name[.="U1"]
operation delete
}
agt_cb: Enter run_trans_complete
agt_cb: Enter sa_run_trans_complete
Clearing current txid for running config
ses: free scb: andy@127.0.0.1 sid: 3 fd: 0
agt_rpc: sending ok <rpc-reply> for ses 3 msg '4'
ses_msg: send 1.1 buff:144 for s:3
trace_buff:
#134
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc-reply message-id="4"
xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<ok/>
</rpc-reply>
agt_audit: skip audit record for RPC summary
agt_cb: Enter run_command_complete
agt_top: end dispatch yuma-netconf:rpc
ses_msg: free msg 0x55c539d8c640 for session 3
RPC Data Output Handling
RPC operations can return data to the client if the operation succeeds. The YANG “output” statement defines the return data for each RPC operation. Constructing YANG data is covered in detail elsewhere. This section shows a simple example SIL invoke function that returns data.
The output data is usually constructed with APIs like agt_make_leaf from
agt/agt_util.h.
To use these APIs, the output object is needed.
Starting in release 23.10-6, the following API is available:
-
obj_template_t *agt_get_rpc_output_obj(rpc_msg_t *msg)
Get the rpc output object template.
OK for SIL; NOT OK for SIL-SA
- Parameters:
msg -- RPC message to check
- Returns:
output object or NULL if some error
This function will provide the parent object for any data objects returned in the RPC output section.
The code generated for the RPC 'invoke' function will include the following code:
obj_template_t *outputobj = agt_get_rpc_output_obj(msg);
if (outputobj == NULL) return ERR_NCX_OPERATION_FAILED;
The 'outputobj' variable can be used as the 'parentobj' parameter for the 'agt_make_*' family of APIs.
For releases prior to 23.10-6, the following code can be used to get this object:
obj_template_t *obj = RPC_MSG_METHOD(msg);
if (obj) {
obj = obj_find_child(obj, NULL, NCX_EL_OUTPUT);
}
if (obj == NULL) {
return ERR_NCX_DEF_NOT_FOUND; // should not happen
}
Once this object template is retrieved from the 'msg' parameter data can be added to the 'msg' using val_value_t structures.
The following snippet shows a leaf being created using an int32 value:
int32 result = 42;
val_value_t *val =
agt_make_int_leaf(obj,
y_addrpc_N_sum,
result,
&res);
After the value is created it must be added to the message using the 'agt_rpc_add_return_val' API:
-
void agt_rpc_add_return_val(val_value_t *return_val, rpc_msg_t *msg)
Add a return value to the msg.
- Parameters:
return_val -- value to add
msg -- message to add value into
if (val) {
agt_rpc_add_return_val(val, msg);
}
RPC Data Output Example
Example YANG Module:
module addrpc {
namespace "http://www.yumaworks.com/ns/addrpc";
prefix add;
revision "2020-02-25";
rpc add {
description "Get the sum of two numbers";
input {
leaf num1 {
type int32;
mandatory true;
description "First number to add";
}
leaf num2 {
type int32;
mandatory true;
description "Second number to add";
}
}
output {
leaf sum {
type int32;
mandatory true;
description "The sum of the 2 numbers";
}
}
}
}
Example SIL Invoke Function Returning Output Data:
/********************************************************************
* FUNCTION y_addrpc_add_invoke
*
* RPC invocation phase
* All constraints have passed at this point.
* Call device instrumentation code in this function.
*
* INPUTS:
* see agt/agt_rpc.h for details
*
* RETURNS:
* error status
********************************************************************/
static status_t y_addrpc_add_invoke (
ses_cb_t *scb,
rpc_msg_t *msg,
xml_node_t *methnode)
{
status_t res = NO_ERR;
if (LOGDEBUG) {
log_debug("\nStart SIL invoke rpc <add> from module addrpc");
}
val_value_t *inputval = agt_get_rpc_input(msg);
if (inputval == NULL) return ERR_NCX_OPERATION_FAILED;
val_value_t *v_num1_val = NULL;
int32 v_num1 = 0;
val_value_t *v_num2_val = NULL;
int32 v_num2 = 0;
v_num1_val = val_find_child(
inputval,
y_addrpc_M_addrpc,
y_addrpc_N_num1);
if (v_num1_val) {
v_num1 = VAL_INT(v_num1_val);
}
v_num2_val = val_find_child(
inputval,
y_addrpc_M_addrpc,
y_addrpc_N_num2);
if (v_num2_val) {
v_num2 = VAL_INT(v_num2_val);
}
/* remove the next line if scb is used */
(void)scb;
/* remove the next line if methnode is used */
(void)methnode;
/* invoke your device instrumentation code here */
/* Following output nodes expected:
* leaf sum
*/
int32 result = v_num1 + v_num2;
obj_template_t *obj = RPC_MSG_METHOD(msg);
if (obj) {
obj = obj_find_child(obj, NULL, NCX_EL_OUTPUT);
}
if (obj == NULL) {
return ERR_NCX_DEF_NOT_FOUND; // should not happen
}
val_value_t *val =
agt_make_int_leaf(obj,
y_addrpc_N_sum,
result,
&res);
if (val) {
agt_rpc_add_return_val(val, msg);
}
return res;
} /* y_addrpc_add_invoke */
RPC Post Reply Callback Function
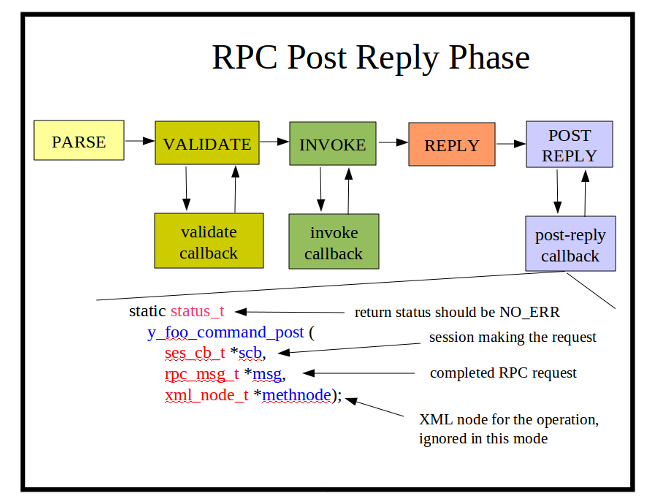
The RPC post-reply callback function is used to clean up after a message has been processed. Only 1 function can register for each YANG rpc statement. The standard NETCONF operations are reserved by the server engine. This callback is not needed unless the SIL validate or invoke callback allocated some memory that needs to deleted after the <rpc-reply> is sent.
The RPC post reply callback function is optional to use. It is enabled with the 'agt_rpc_register_method' function, within the phase 1 initialization callback function.
The yangdump-pro code generator will not create this SIL callback function by default.
Example SIL Function Registration
Example SIL Function:
/********************************************************************
* FUNCTION y_foo_command_post
*
* RPC post reply phase
*
* INPUTS:
* see agt/agt_rpc.h for details
*
* RETURNS:
* error status
********************************************************************/
static status_t
y_foo_command_post (
ses_cb_t *scb,
rpc_msg_t *msg,
xml_node_t *methnode)
{
(void)scb;
(void)methnode;
if (msg->rpc_user1 != NULL) {
m__free(msg->rpc_user1);
msg->rpc_user1 = NULL;
}
return NO_ERR;
} /* y_foo_command_post */
Datastore Edit APIs For RPC SIL Callbacks
Note
This feature is available starting in 23.10-2
The APIs in this section must only be used from within SIL callback code for YANG RPCs and actions
Usage
A custom RPC (or action) callback can edit the server configuration using APIs similar to the Database Edit APIs for DB-API subsystems.
These APIs must be used with care, especially the option to treat the datastore edit as a 'system edit'.
The APIs in this section follow the same pattern as the DB-API functions for Database Edits Using YANG Patch.
There are 5 steps needed to use this database editing method:
Restrictions
These APIs can be found in 'agt_util.h' and only used with the netconfd-pro process. They will not work if used from a different process.
There are not many restrictions for this mode of datastore editing. That is why its usage should be done with extreme caution. There are two parameters that require special attention:
The 'system_edit' flag should be set to 'false' in almost all cases. If 'true' then access control will be bypassed.
The 'skip_sil' flag should be set with great care. Any edit that changes data managed by server SIL callbacks must not set this flag to 'true'.
The edit transaction will cause an audit log update and config-change notification to be sent. This may be done before the <rpc-reply> for the original RPC request is done.
Start Patch Edit Request
The SIL callback must start a patch edit control block as the first step.
Dynamic Edit Parms
The edit parms control block can be malloced and then freed after the edit is applied the server.
Use agt_new_edit_parms to create
-
agt_edit_parms_cb_t *agt_new_edit_parms(const xmlChar *patch_id_str, boolean system_edit, boolean skip_sil, const xmlChar *comment)
Example:
const xmlChar *patch_id_str = (const xmlChar *)"MyPatch1";
const xmlChar *comment = (const xmlChar *)"myComment";
agt_edit_parms_t *parms =
agt_new_edit_parms(patch_id_str,
false, // system_edit
false, // skip_sil
comment);
// .. Use the parms; check ERR_INTERNAL_MEM error if NULL
Static Edit Parms
The edit parms control block can be a static data structure that is cleaned after the edit is applied the server.
Use agt_init_edit_parms to initialize
-
status_t agt_init_edit_parms(agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms, const xmlChar *patch_id_str, boolean system_edit, boolean skip_sil, const xmlChar *comment)
Example:
agt_edit_parms_t parms;
const xmlChar *patch_id_str = (const xmlChar *)"MyPatch1";
const xmlChar *comment = (const xmlChar *)"myComment";
status_t res =
agt_init_edit_parms(&parms,
patch_id_str,
false, // system_edit
false, // skip_sil
comment);
// .. Use the parms; check ERR_INTERNAL_MEM error if NULL
Add Edits to Patch Edit Request
The 'agt_add_patch_edit' function is used to add edits to the YANG Patch edit to the edit transaction.
This must be done after an 'agt_edit_parms_t' struct is created or initialized.
This must be done before the 'agt_apply_patch_edit' function is invoked.
The 'system_edit' and 'skip_sil' parameters apply to all edits in the edit transaction, so be careful about combining edits in the same patch request.
The 'edit_id_str' parameter must be unique for each edit. The actual values are not important, but they are used as YANG key leaf values.
The 'edit_target' expression does not need prefixes if the referenced data nodes do not have any duplicate local-name sibling nodes.
When submitting an edit to the <operational> datastore using the Operational Datastore Push Mode, specific parameters must be configured to ensure the edit is processed correctly. Refer to Operational Datastore Specific Parameters for more details.
-
status_t agt_add_patch_edit(agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms, const xmlChar *edit_id_str, const xmlChar *edit_target, const xmlChar *edit_operation, const xmlChar *edit_xml_value, const xmlChar *insert_point, const xmlChar *insert_where)
Create an edit request and add to YANG Patch in progress.
THIS API MUST ONLY BE USED WITHIN THE MAIN SERVER.
OK for SIL; NOT OK for SIL-SA
See also
db_api_add_edit
- Parameters:
parms -- edit parms in progress
edit_id_str -- index value for the edit
edit_target -- edit target path string
edit_operation -- edit operation (create merge replace delete remove)
edit_xml_value --
XML payload in string form, whitespace allowed
MAY BE NULL if no value required (delete remove))
insert_point -- a string like the target except a different instance of the same list of leaf-list; only for before, after; NULL if not used
insert_where -- == <insert enum string> (may be NULL if not used)
"before"
"after"
"first"
"last"
- Returns:
status
Example:
const xmlChar *edit_id_str = (const xmlChar *)"edit1";
const xmlChar *edit_target - (const xmlChar *)"/int8.1";
const xmlChar *edit_operation = (const xmlChar *)"merge";
const xmlChar *edit_xml_value = (const xmlChar *)
"<int8.1 xmlns='http://netconfcentral.org/ns/test'>22</int8.1>";
status_t res =
agt_add_patch_edit(parms,
edit_id_str,
edit_target,
edit_operation,
edit_xml_value,
NULL, // insert_point
NULL); // insert_where
Apply Patch Edit to Server
The 'agt_apply_patch_edit' is used to apply the edit transaction to the server after all the individual edits have been added.
The 'scb' parameter should be the one for the session that is invoking the RPC operation or YANG action.
This function can fail for many reasons:
Any datastore operation is already in progress
Any configuration datastore is not ready to be written
The 'edit_xml_value' string is provided and does not parse correctly, based on the 'edit_target' string
Any normal configuration validation error can occur depending on the edit request
-
status_t agt_apply_patch_edit(ses_cb_t *scb, agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms)
SIL version of the db_api_send_edt_full2 API.
OK for SIL; NOT OK for SIL-SA
Create a YANG Patch edit request and invoke it locally. This patch can have exactly one edit. Provides full access to all 1-shot send_edit parameters.
THIS API MUST ONLY BE USED WITHIN THE MAIN SERVER.
See also
db_api_send_edit_full2
- Parameters:
scb -- session control block for real session that is altering the datastore as a side effect of the RPC operation in progress
parms -- == agt_edit_parms_cb_t struct
MUST BE INITIALIZED FIRST WITH agt_init_edit_parms
- Returns:
status
Example:
res = agt_apply_patch_edit(scb, parms);
Cleanup the Patch Edit
The patch edit parms are not needed after the edit is applied.
If a dynamic edit parms control block is created it must be freed.
If a static edit parms control block is initialized it must be cleaned.
Dynamic Edit Parms
Use agt_free_edit_parms to free the edit parms control block.
-
void agt_free_edit_parms(agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms)
Example:
agt_free_edit_parms(parms);
Static Edit Parms
Use agt_clean_edit_parms to clean
-
void agt_clean_edit_parms(agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms)
Example:
agt_clean_edit_parms(&parms);
RPC Example: Add NACM Edit from a Custom RPC
This example demonstrates how these APIs can be used to update the NACM 'group' configuration when the custom RPC 'add-user' is invoked.
The client invokes the 'add-user' RPC and the
/nacm/groupssubtree is updated with the proper configuration.
YANG For the add-user RPC
rpc add-user {
input {
leaf group {
type yang:yang-identifier;
mandatory true;
}
leaf user {
type yang:yang-identifier;
mandatory true;
}
}
}
Prepare Steps
Make sure the YANG module 'test/pass/testrpc.yang' is present on the system and found by yangdump-pro.
Run the make_sil_dir_pro script to generate the stub code
> make_sil_dir_pro testrpc
Add the 'add_nacm_user' function to the file 'u_testrpc.c'
Change the 'add_user_validate' and 'add_user_invoke' functions to extract the parameters and invoke the 'add_nacm_user' function
add_nacm_user Function
This function contains all the API examples from this section.
The
NACMXMLtemplate is used to create a simple XML snippet to merge into the/nacm/groupssubtree.The last term in the 'edit_xml_value' string must match the top-level XML element in the 'edit_xml_value' parameter
Set the 'edit_xml_value' parameter to
NULLif the 'edit_operation' string is equal todeleteorremoveUse 'system_edit' set to
falseto make this a user edit.Use 'skip_sil' set to
falsesince the NACM module is implemented by the server and the SIL callbacks must be invoked to activate the configuration.
/**
* @brief Use the SIL datastore edit APIs to add a NACM user
*
* @param group NACM group name
* @param user NACM user name
* @return return status
*/
static status_t
add_nacm_user (ses_cb_t *scb,
const xmlChar *group,
const xmlChar *user)
{
status_t res = NO_ERR;
/* set parameters for this example edit
* - treat as a user edit
* - do not skip NACM SIL or group/user will not be used
*/
const xmlChar *patch_id_str = (const xmlChar *)"test-rpc-patch";
boolean system_edit = false;
boolean skip_sil = false;
const xmlChar *comment = (const xmlChar *)"add-user edit";
/* step 1: start a YANG Patch edit */
agt_edit_parms_cb_t *parms =
agt_new_edit_parms(patch_id_str,
system_edit,
skip_sil,
comment);
if (parms == NULL) {
return ERR_INTERNAL_MEM;
}
/* step 2: add 1 or more edits
* - do not need to check any existing config first for this edit
* - picking the groups container as the start of the merge
* - Using a strncpy buffer to fill a simple XML template
*/
#define XMLBUFFLEN 512
char value_buff[XMLBUFFLEN];
*value_buff = 0;
#define NACMXML \
"<groups><group><name>%s</name><user-name>%s</user-name></group></groups>"
/* create the edit_xml_value parameter first */
int ret = snprintf(value_buff,
XMLBUFFLEN,
NACMXML,
(const char *)group,
(const char *)user);
if (ret <= 0) {
res = ERR_NCX_OPERATION_FAILED;
}
const xmlChar *edit_id_str = (const xmlChar *)"E1";
const xmlChar *edit_target = (const xmlChar *)"/nacm/groups";
const xmlChar *edit_operation = (const xmlChar *)"merge";
const xmlChar *edit_xml_value = (const xmlChar *)value_buff;
const xmlChar *insert_point = NULL;
const xmlChar *insert_where = NULL;
if (res == NO_ERR) {
res = agt_add_patch_edit (parms,
edit_id_str,
edit_target,
edit_operation,
edit_xml_value,
insert_point,
insert_where);
}
if (res == NO_ERR) {
/* Step 3: Apply the edit */
res = agt_apply_patch_edit(scb, parms);
}
/* step 4: cleanup */
agt_free_edit_parms(parms);
return res;
} /* add_nacm_user */
RPC Validate Function Changes
The 'u_trpc_add_user_validate' function is altered to check the maximum group and user name string lengths.
/* RPC Input: group */
v_group_val = val_find_child(
inputval,
y_trpc_M_trpc,
y_trpc_N_group);
if (v_group_val) {
v_group = VAL_STRING(v_group_val);
if (xml_strlen(v_group) > NCX_MAX_NCXNAME_LEN) {
res = ERR_NCX_TOO_BIG;
errorval = v_group_val;
}
}
/* RPC Input: user */
if (res == NO_ERR) {
v_user_val = val_find_child(
inputval,
y_trpc_M_trpc,
y_trpc_N_user);
if (v_user_val) {
v_user = VAL_STRING(v_user_val);
if (xml_strlen(v_user) > NCX_MAX_NCXNAME_LEN) {
res = ERR_NCX_TOO_BIG;
errorval = v_user_val;
}
}
}
RPC Invoke Function Changes
The 'u_trpc_add_user_invoke' function is altered to invoke the 'add_nacm_user' function to apply the NACM edit.
/* invoke your device instrumentation code here */
res = add_nacm_user(scb, v_group, v_user);
RPC Invocation Example
In this example, the client is invoking add-user for group 'G1' and user 'U1'.
> add-user group=G1 user=U1
The XML for this request may look as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc message-id="3"
xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<add-user xmlns="urn:yumaworks:params:xml:ns:yang:testrpc">
<group>G1</group>
<user>U1</user>
</add-user>
</rpc>
The server log shows the complete transaction (e.g. same as an <edit-config> operation), and if successful, will include a section from 'agt_yangapi_edit' similar to the following:
agt_yangapi_edit: <config> content:
yuma-netconf:config {
ietf-netconf-acm:nacm {
groups {
group G1 {
name G1
user-name U1
}
}
}
}
Example Audit Log Entry
If successful, there will may be an audit log entry for the added edit, similar to the following:
edit-transaction 9384: on session 3 by andy@127.0.0.1
time: 2023-10-23T01:21:49Z
message-id: --
trace-id: --
datastore: running
operation: create
target: /nacm:nacm
comment: add-user edit
Example Successful Response
If successful, the 'rpc-reply' for the 'add-user' request will be sent back to the client.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rpc-reply message-id="3"
xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<ok/>
</rpc-reply>
The 'running' configuration returned from a <get-config> operation will contain the newly added configuration, which may look as follows:
<data>
<nacm xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:yang:ietf-netconf-acm">
<groups>
<group>
<name>G1</name>
<user-name>U1</user-name>
</group>
</groups>
</nacm>
</data>
Example Error Response
In this example, the 'candidate' datastore is locked by another user which will cause the 'add-user' operation to fail. In this case an 'rpc-error' will be returned, that may appear as follows:
<rpc-reply message-id="3" xmlns:ncx="http://netconfcentral.org/ns/yuma-ncx"
xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<rpc-error>
<error-type>rpc</error-type>
<error-tag>in-use</error-tag>
<error-severity>error</error-severity>
<error-app-tag>no-access</error-app-tag>
<error-path>/add-user</error-path>
<error-message xml:lang="en">config locked</error-message>
<error-info>
<error-number>301</error-number>
</error-info>
</rpc-error>
</rpc-reply>