ZMQAPI Command Channel
The 'yangcli-gw' command channel is used to access the yangcli-pro command processing features.
There is a single, serialized command state, just like within the yangcli-pro application.
The current state of the gateway is important, since any command sent in a client request (REQ) message will be executed in the current context.
The basic steps are the same as in yangcli-pro, except the input is derived from a ZeroMQ message instead of the 'libtecla' command line.
Your application sends a REQ message to yangcli-gw
yangcli-gw validates the request and invokes the command in the current session context (if connected)
Your application receives a yangcli-gw response (REP) message
The first word of all ZMQAPI messages contains the protocol name and the version number. This document defines version 1 of the protocol.
The version string
ZMQAPI.1is used to identify this version of the protocol.
REQ/REP Message Flow
The message flow for the command channel is a simple request and response pair.
The application sends a ZMQAPI REQ Message to yangcli-gw
yangcli-gw sends a ZMQAPI REP Message to the application
The ZeroMQ socket specified by the --zmqapi-responder-endpoint parameter is used for this message flow.
ZMQAPI REQ Message
The request is a multi-part message that has one header and one or more message parts.
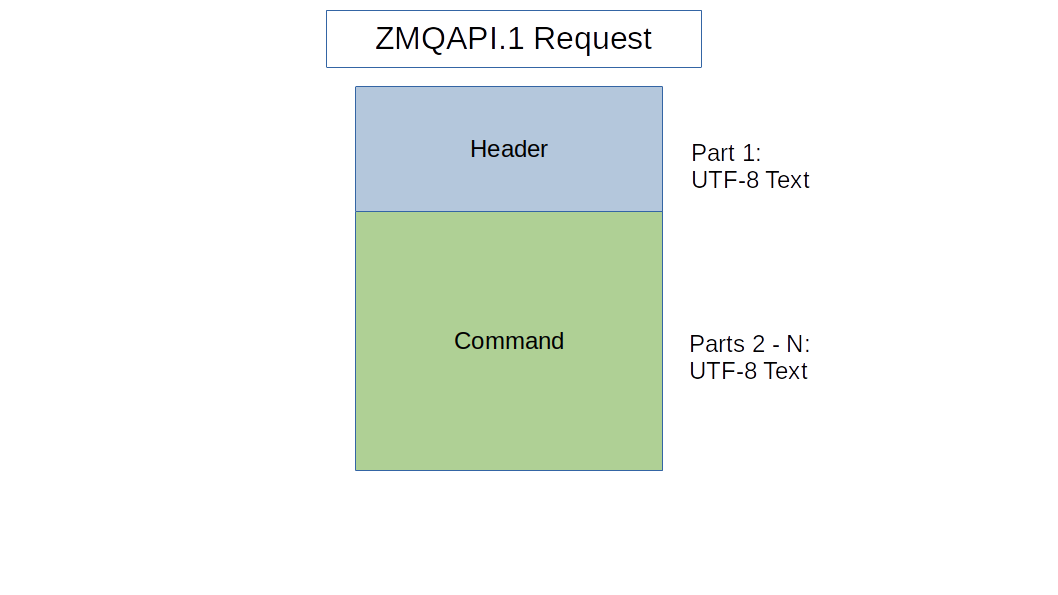
Message Part |
Description |
ZMQAPI header |
Text header line defining the message to follow |
Command Line |
Text representing the yangcli-pro command line. If more than one message part is sent after the ZMQAPI header then they all will be concatenated to form the command line. |
ZMQAPI REQ Header
The ZMQAPI header used in a 'REQ' message has four fields:
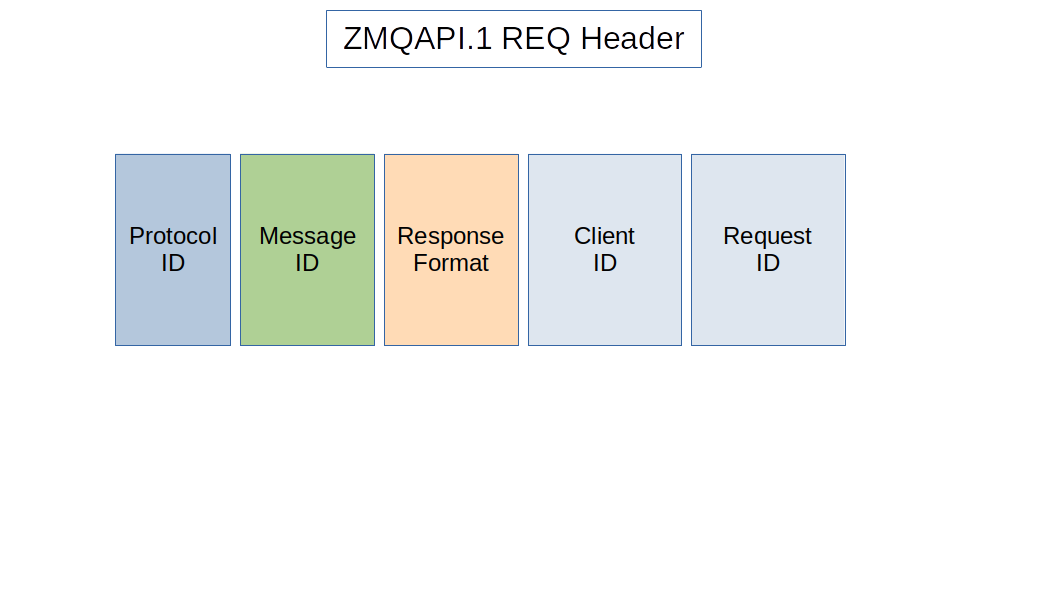
ZMQAPI Header Fields For REQ Message
Protocol ID: Text contains the string
ZMQAPI.1.Message ID: Text contains the string
REQ.Response Format: Payload format that is requested in the server response message.
Any valid ZMQAPI Response Format code can be used
Use value
R0to suppress the Response Payload and Logging Output message parts in the gateway response message. This will be the return response format if the gateway returns only headers and no payload or logging message parts.The value
R1should be used for text output. This will be the return response format if the gateway returns a text status message.The value
R2should be used for the best JSON compatibility with programming tools.The value
R3should be used if IETF JSON can be parsed correctly by the programming tools.
Client ID: Text string identifying the client application.
This field is optional and can be omitted.
The client ID should be a string from 1 to 64 characters, using 'yang-identifier' syntax. No strict format is enforced.
If present, it will be returned in the server response message sent by yangcli-gw
It is possible this field will be truncated in the server response if the header length would exceed 4095 bytes.
Request ID: Text string identifying the request message.
This field is optional and can be omitted.
Simple text is permitted and may contain client state
The request ID should be a UUID string. No strict format is enforced.
If present, it will be returned in the server response message sent by yangcli-gw.
It is possible this field will be omitted or truncated in the server response if the header length would exceed 4095 bytes.
Example REQ Header
ZMQAPI.1 REQ R2 client1 edb5debc-1dc7-11ee-be86-e9f635d13331
In this example, the following fields are present:
Protocol ID:
ZMQAPI.1Message ID:
REQResponse Format:
R2Client ID:
client1Request ID:
edb5debc-1dc7-11ee-be86-e9f635d13331
ZMQAPI REQ Command
The request command is a text command which must contain one or more lines of text that represent one yangcli-gw command.
The maximum length of a yangcli-gw command is one less than one megabyte (1048575) characters.
Line length limitations for specific commands may not support a line length above 64 KBytes in length
Large commands can be avoided by using external XML data files
If the command is sent in multiple parts, then they will be concatenated to form one command buffer.
ZMQAPI Dot Commands begin with the period (.) character. These are reserved commands that are sent to the yangcli-gw message processor, not the command line processor.
A normal command is processed by yangcli-gw in the same way as a yangcli-pro command, with some limitations:
Only 'batch mode' operation is permitted, as if the --batch-mode CLI parameter is set to 'true'.
The interactive fill command mode is not allowed.
Tab completion is not available.
Command line pipe commands are not available
yangcli-gw will send a
REPserver response message when the command processing is completed.
ZMQAPI REP Message
The response is a multi-part message that has two headers, and usually one payload part and one logging part.
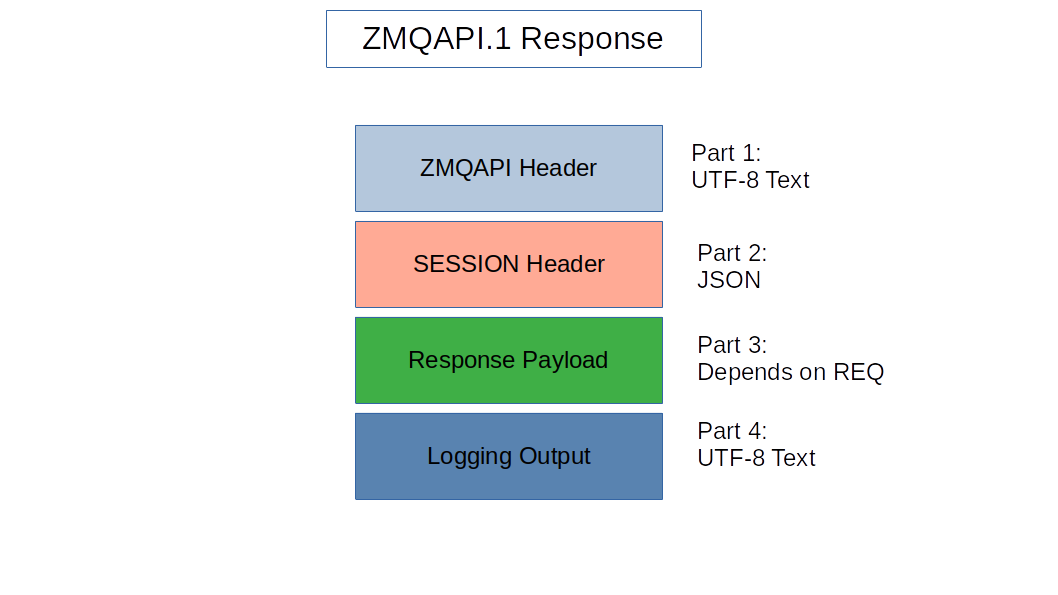
Message Part |
Description |
ZMQAPI header |
Text header line defining the message to follow |
SESSION header |
JSON header containing session status info |
Response Payload |
Section will be present and encoded in the
requested format if status |
Logging Output |
Text section containing the logging output.
Omitted if REQ Response Type is |
ZMQAPI REP Header
The ZMQAPI header used in a 'REP` message has seven fields:
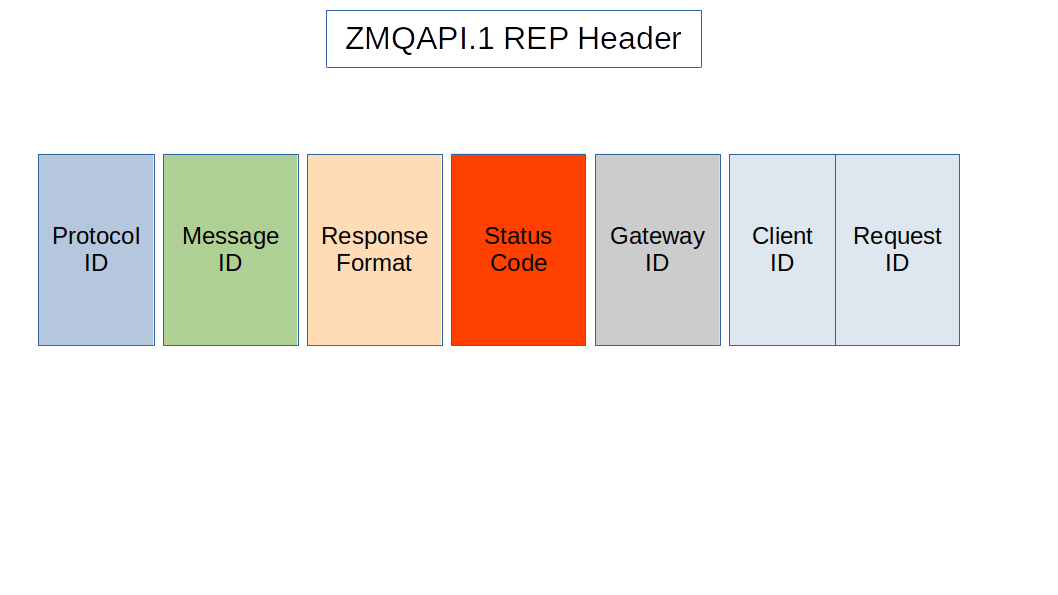
ZMQAPI Header Fields For REP Message
Header Field |
Description |
Protocol ID |
Text contains the string |
Message ID |
Text code contains the string |
Response Format |
Text code representing the payload format in the payload section. |
Status Code |
Text string representing the return status code. |
Gateway ID |
Text string identifying the gateway. |
Client ID |
Client ID provided in REQ message (if any). |
Request ID |
Request ID provided in REQ message (if any). |
Example REP Header
ZMQAPI.1 REP R2 S0 gateway1 client1 edb5debc-1dc7-11ee-be86-e9f635d13331
In this example, the following fields are present:
Protocol ID:
ZMQAPI.1Message ID:
REPResponse Format:
R2Status Code:
S0Gateway ID:
gateway1Client ID:
client1Request ID:
edb5debc-1dc7-11ee-be86-e9f635d13331
ZMQAPI REP SESSION Header
The Server Response Message always contains a ZMQAPI SESSION Header. If the current session is connected at the end of the command execution, then the connected session information is returned in this header.
ZMQAPI REP Response Payload
The content and format of this message part depends on the request and result of processing the request:
If the Response Format in the ZMQAPI header is
R0then the response payload is not presentif the Status Code in the ZMQAPI header is not
S0then the requested Response Format may be changed toR1and this section will contain an error message corresponding to the error statusIn all cases the Response Format code returned in the ZMQAPI header will identify the actual encoding format of the response payload section
For Show Commands this section should contain the status
okand the actual show command output will be in the logging output
Example: REP Message For OK Status
Command: show var message-indent
ZMQAPI.1 REP R1 S0 gateway1 client1 c1f2b8b6-5014-11ee-931b-63c97bc4bbbc
{"count":1,"sid":1,"name":"default","server":"localhost","port":830,"user":"andy"}
ok
andy@localhost> show var message-indent
message-indent 1
Example: REP Message for an Error Status
Command: some-bad-command
ZMQAPI.1 REP R1 S250 gateway1 client1 eda172e6-5013-11ee-931b-63c97bc4bbbc
{"count":1,"sid":1,"name":"default","server":"localhost","port":830,"user":"andy"}
definition not found
andy@localhost> some-bad-command
Error: Unrecognized command
Example: REP Message for a Data Response
Command: xget /netconf
ZMQAPI.1 REP R2 S0 gateway1 client1 09747fbc-5015-11ee-931b-63c97bc4bbbc
{"count":1,"sid":1,"name":"default","server":"localhost","port":830,"user":"andy"}
{
"rpc-reply": {
"data": {
"netconf": {
"streams": {
"stream": [
{
"name":"NETCONF",
"description":"default NETCONF event stream",
"replaySupport":true,
"replayLogCreationTime":"2023-09-10T19:04:40.916509Z"
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
andy@localhost> xget /netconf
RPC Data Reply 6 for session 5 [default]:
ZMQAPI REP Logging Output
The content and format of this message part depends on the request and result of processing the request:
If the Response Format in the ZMQAPI header is
R0then the logging output is not presentThe contents of this section will depend on the --log-level and other logging parameters
A separate copy of the logging output is generated for the REP message which may not be the exact same contents of the --log file, if it is used in yangcli-gw.
If yangcli-gw is running without any --log parameter, then logging output will only be output to STDOUT for errors and warnings, unless the --log-level parameter is set to 'debug' or higher.
Complete logging info is sent to yangcli-gw, which includes log-level='info' output
ZMQAPI Dot Commands
There are special commands that are meant for the yangcli-gw processing engine, not the yangcli-pro command interpreter. These are called 'dot' commands because they begin with the dot '.' character.
All yangcli-pro and NETCONF server commands must use a valid YANG identifier, which cannot begin with a dot character.
ZMQAPI Dot Status Command
This command consists of a single dot character '.'. When received by yangcli-gw, a Server Command Response will be sent which consists of:
Example
Client sends a ZMQAPI REQ message in two parts:
Part 1: ZMQAPI REQ header
ZMQAPI.1 REQ R2 client1 e9cbc294-1e8a-11ee-be86-e9f635d13331
Part 2: ZMQAPI Command
.
yangcli-gw sends a ZMQAPI REP message in two parts:
Part 1: ZMQAPI REP header
ZMQAPI.1 REP R0 S0 gateway1 client1 e9cbc294-1e8a-11ee-be86-e9f635d13331
Part 2: ZMQAPI SESSION header
{"count":1,"sid":1,"name":"default","server":"localhost","port":830,"user":"andy"}
Notes:
The response type
R0is sent in the response even though the request asked for theR2response type. The response type will always beR0if no payload section is sent in the response.The status
S0is always sent in a response for a Dot Status command.The SESSION header is encoded as a simple JSON dictionary. There is no parent container object.
ZMQAPI yangcli Commands
Most yangcli-pro commands are allowed in yangcli-gw.
Refer to the Invoking yangcli-pro Commands section for background on yangcli-pro commands, Note that interactive commands and features are not supported in yangcli-gw.
Refer to the Using External XML section for details on using external data files.
Refer to the yangcli-pro Command Reference for the full set of commands. (Note that not all commands are available in yangcli-gw)
Note
Interactive commands such as fill are not supported
Command line Pipe Commands are not supported
Plain Commands
Plain commands usually return 'OK' or sometimes print an Error message.
These are usually local commands but could be a server command such as lock
In the examples below, the response message is
okin both cases.For the local command the logging shows
OKFor the server command the logging shows
RPC OK Reply 3 for session 4 [default]:
Example: Set a system variable
Enter yangcli-gw command: $$message-indent=2
Send header
ZMQAPI.1 REQ R2 client1 5cf2fe70-4778-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Send command
$$message-indent=2
Got 4 REP message parts
Received ZMQAPI header
ZMQAPI.1 REP R2 S0 gateway1 client1 5cf2fe70-4778-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Received SESSION header
{"count":1,"sid":3,"name":"default","server":"192.168.0.237","port":830,"user":"andy"}
Received response message
ok
Received log message
System variable set
andy@192.168.0.237> $$message-indent=2
OK
Enter yangcli-gw command:
Example: Invoke the <lock> Operation
Enter yangcli-gw command: lock target=candidate
Send header
ZMQAPI.1 REQ R2 client1 9f767b4a-477e-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Send command
lock target=candidate
Got 4 REP message parts
Received ZMQAPI header
ZMQAPI.1 REP R2 S0 gateway1 client1 9f767b4a-477e-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Received SESSION header
{"count":1,"sid":4,"name":"default","server":"192.168.0.237","port":830,"user":"andy"}
Received response message
ok
Received log message
andy@192.168.0.237> lock target=candidate
RPC OK Reply 3 for session 4 [default]:
Show Commands
Show commands are always local commands.
For yangcli-gw access the return value is always 'ok' (unless some error)
The show command output will be in the Logging output section
Example: show session
Enter yangcli-gw command: show session
Send header
ZMQAPI.1 REQ R2 client1 6226024a-4776-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Send command
show session
Got 4 REP message parts
Received ZMQAPI header
ZMQAPI.1 REP R2 S0 gateway1 client1 6226024a-4776-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Received SESSION header
{"count":1,"sid":3,"name":"default","server":"192.168.0.237","port":830,"user":"andy"}
Received response message
ok
Received log message
andy@192.168.0.237> show session
NETCONF 1.1 session established for andy on 192.168.0.237
Client Session Id: 3
Server Session Id: 3
Server Protocol Capabilities
base:1.0
base:1.1
candidate:1.0
confirmed-commit:1.0
confirmed-commit:1.1
interleave:1.0
notification:1.0
partial-lock:1.0
rollback-on-error:1.0
url:1.0
validate:1.0
validate:1.1
with-defaults:1.0
xpath:1.0
yang-library:1.0
Server Module Capabilities
*** rest of output truncated ***
Enter yangcli-gw command:
Example: show var message-indent
Enter yangcli-gw command: show var message-indent
Send header
ZMQAPI.1 REQ R2 client1 507ef412-477f-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Send command
show var message-indent
Got 4 REP message parts
Received ZMQAPI header
ZMQAPI.1 REP R2 S0 gateway1 client1 507ef412-477f-11ee-9cdf-257b3af3daaa
Received SESSION header
{"count":1,"sid":4,"name":"default","server":"192.168.0.237","port":830,"user":"andy"}
Received response message
ok
Received log message
andy@192.168.0.237> show var message-indent
message-indent 2
Enter yangcli-gw command:
Data Commands
Data commands are server operations which return data, such as the <get> or <get-data> operations.
The Response Payload part of the message will contain the requested data if the Response Status Code is
S0The server response will be encoded according to the format requested in the ZMQAPI REQ Message in the Response Format field
The data will not be repeated in the Logging Output section unless the --log-level is set to 'debug' or higher.
Using Scripts and Data Files
yangcli-gw uses the same file locations as yangcli-pro for script and data files.
The --datapath can be used at boot-time to set additional file search paths for data files.
The --runpath can be used at boot-time to set additional file search paths for script files.
Script and data files can be created and used at run-time. They do not have to be in place at boot-time.
Script and Data files are not cached by yangcli-gw.
It is safe to insert a script or data file into the search path at runtime.
yangcli-gw will only search for the requested file only when it is used