
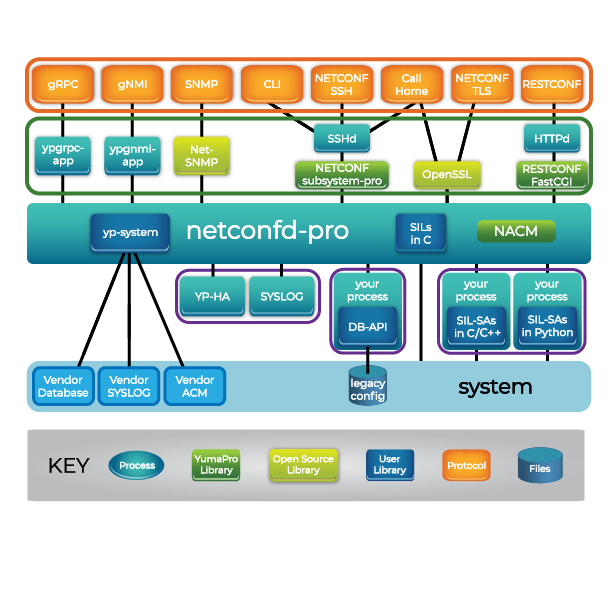
netconfd-pro Introduction
The netconfd-pro program is a NETCONF-over-SSH server implementation. It is driven directly by YANG files, and provides a robust and secure database interface using standard NETCONF protocol operations.
All aspects of NETCONF protocol operation handling can be done automatically by the netconfd-pro server. However, the interface between the NETCONF database and the device instrumentation is not covered in this document. Refer to the YumaPro Developer Manual for details on adding YANG module instrumentation code to the netconfd-pro server.
netconfd-pro Features
The netconfd-pro server has the following features:
Protocol Features
NETCONF
Complete implementation of NETCONF versions 1.0 (RFC 4741) and 1.1 (RFC 6241).
Automatic support for all NETCONF Protocol Operations, including the YANG 'insert' operation. (RFC 7950)
Supports the complete SSH transport binding defined in RFC 4742 and RFC 6242, using the industry standard OpenSSH server.
The netconf-subsystem-pro program is invoked as an SSH subsystem. This connects the OpenSSH server to the netconfd-pro server for NETCONF over SSH sessions.
Supports the complete NETCONF Over TLS transport binding defined in RFC 7589, using the industry standard OpenSSL libraries
The NETCONF over TLS sessions are handled directly by netconfd-pro. There are extensive TLS Configuration parameters to setup the TLS server in many different ways.
Confirmed Commit capability for robust multi-device edit transactions with automatic rollback.
RESTCONF
Supports the RESTCONF Protocol defined in RFC 8040, using industry-standard WEB servers
The restconf program is invoked as a FastCGI subsystem. This connects the HTTPS server to the netconfd-pro server for RESTCONF sessions.
Supports the YANG Patch Media Type defined in RFC 8072, to allow complex incremental configuration editing in addition to REST editing APIs
Supports RESTCONF Notifications defined in RFC 8040
Supports all RESTCONF Resource Types, Headers, and Query Parameters
Supports Operation Resource so any YANG 'rpc' operation can be invoked
Supports YANG Actions so any YANG 'action' can be invoked
Supports RESTCONF Subscriptions defined in RFC 8650
XML and JSON encoding with full <establish-subscription> parameters for all Event Streams and YANG Push
Other Protocols
Supports the IETF Call Home for NETCONF feature defined in RFC 8071
Supports Schema Mount data models, using the YANG extensions defined in RFC 8528
Dedicated CLI
Built in YANG automation
High-level easy-to-use commands
Config Mode configuration editing
Dedicated WEB-UI
Binary Push: CBOR Encoding of Notification Messages (RFC 9254)
Supports YANG SID files (RFC 9595) including retrieval from the server
Supports Notifications over UDP-Notif Protocol
Supports YANG Push 2 features (DRAFT)
Server Platform Services
Datastores
Supports the Network Management Datastore Architecture (NMDA) defined in RFC 8342 and RFC 8526
Supports <candidate>, <running>, and <startup> Databases, fully-configurable with CLI parameters.
Full support for database locking, editing, validation, including extensive user-callback capabilities to support device instrumentation.
Fully recoverable, automatic database editing, using a simple 3 phase callback model
validate, 2) apply, 3) commit or rollback
Automatic support for all YANG validation mechanisms, including all XPath conditionals
Supports loading and unloading server instrumentation libraries and YANG files at run-time
Automatic subtree and XPath filtering
- Reguler Expression Matching in
subtree content-match expressions
Automatic confirmed-commit and rollback procedures
Automatic database audit log and change notification support
Complete RFC 5717 Partial Lock support with full XPath support, and all partial locking monitoring data defined in ietf-netconf-monitoring.yang.
System Sorted Configuration: YANG and CLI control over automatic sorting of system-ordered lists.
Automatic YANG Metadata support using custom md:annotation statements (RFC 7952)
Compare Databases using the <compare-config> operation from the yumaworks-compare.yang module
Compare Datastores, Backup Files, or URLs
Use XPath or Subtree filter to compare a subset of the datastore.
YANG Patch output
Error Handling
Complete rpc-error reporting support, including user-defined errors via YANG error-app-tag and error-message statements.
Several 'rpc-error' extensions, including <bad-value> and error-number, for easier debugging
Dynamic Error Messages using content from the configuration datastores to fill in custom error messages
Multi-Language Error Messages can be configured and used instead of the default English error messages
Rich set of Error Reporting CLI Parameters to control how the server handles various error conditions
Supports complete control of the '<rpc-error>' content using Error Handling APIs for SIL, SIL-SA, and PY-SIL instrumentation code.
Built-in set of Error Messages that can be replaced at boot-time or runtime
Logging
Multiple independent Logging streams
Comprehensive logging capabilities for easy debugging during YANG content development or normal operation.
SYSLOG Support using built-in or system API library functions
Audit Log with configurable audit log events
Bootstrap CLI to allow some critical CLI parameters to take effect immediately (before the YANG compiler and other services are ready)
Special PTHREADS logging support
Support for logrotate integration
Notifications
Complete RFC 5277 Notification support, including notification replay, :interleave capability, and mandatory 'NETCONF' event stream
Several useful built-in notifications
Supports dynamic Notification Subscriptions defined in RFC 5277 and RFC 8639,
Supports YANG 1.1 Nested Notification Messages defined in RFC 7950
Supports Dynamic Subscription to YANG Events and Datastores over NETCONF, defined in RFC 8640
Supports Dynamic Subscriptions to Event Streams defined in RFC 8639
Supports YANG Push Dynamic subscriptions to datastores defined in RFC 8641
Complete support for standard NETCONF notification events defined in RFC 6470
Configurable event streams for managing different types of notifications more effectively.
Powerful Send Event APIs for SIL, SIL-SA, and PY-SIL deployment.
Special Developer Callbacks so instrumentation code does not need to waste resources generating and sending notification events if notifications are currently disabled.
Platform
Automatic server state monitoring support. ypwatcher program periodically checks if the server is alive, and if not restart the server and write the event into syslog.
Runtime configuration of CLI parameters. The yumaworks-server.yang YANG module allows all CLI parameters to be edited. Some parameters can be changed at run-time and the rest can be changed to be activated on the next server restart.
Filesystem Hierarchy Standard support when running as root and configured to use FHS.
Comprehensive System Configuration options includes many Environment Variables that control file search locations.
Automatic session management, including configurable number of concurrent sessions, session customization, and all database cleanup.
Maintenance Mode allows server access to be temporarily disabled or restricted while system maintenance is being done.
Multi-Instance Mode: Run multiple instances of the netconfd-pro server and its components on the same host.
yp-system library for easy server integration, providing an extensive set of System Callbacks
-
<factory-reset> operation
Security
Comprehensive, fully NETCONF configurable, access control model, defined in ietf-netconf-acm.yang (RFC 8341).
Session Admission Control support to limit allowed users, concurrent sessions, etc.
Configurable Idle Timeout to drop inactive sessions
Runtime configuration of NETCONF over TLS Certificate to Name Mappings
Full support for RFC 7589 Client Identity certificate processing procedures
yumaworks-cert-usermap.yang uses the 'cert-to-name' grouping from ietf-x509-cert-to-name.yang (RFC 7407)
YANG Automation
Full, automatic run-time support for any YANG-defined content:
rpc statement automatically supported, so new operations can be added at run-time
All YANG data statements automatically supported, so new database objects can be added at run-time
Notification statement automatically supported, so new notification event types can be added at run-time
Automatic support for all Capabilities registration and <hello> message processing
Full, automatic generation of all YANG module <capability> contents, including features and deviations
Full support for all YANG constructs, including deviations
Full support of YANG sub-modules, including nested sub-modules
Multiple concurrent module versions supported (import-by-revision)
Multiple concurrent submodule versions supported (include-by-revision)
Optimized, full XPath 1.0 implementation, including all YANG extensions
Ability to enable or disable any YumaWorks module using configuration parameters
Ability to hide any “internal use” YANG module from northbound clients
Built-in automation for a large set of YANG extensions
Built-in support for OpenConfig YANG Extensions
Supports YANG 1.1 Actions defined in RFC 7950
Complete XML 1.0 implementation with full support for XML Namespaces
Complete JSON for YANG implementation (defined in RFC 7951)
Monitoring Features
Many Monitoring features built-in, but not all enabled by default.
Full implementation of the ietf-netconf-monitoring.yang data model, including the <get-schema> operation to retrieve YANG or YIN modules from the server.
Configurable Default Node Handling, including full support of the <with-defaults> standard, in ietf-netconf-with-defaults.yang.
System information automatically supported, as defined in yuma-system.yang.
Some system APIs automatically supported, as defined in yumaworks-system.yang and ietf-system.yang.
Time filtering support for <get> and <get-config> requests with 'modified-since' and 'if-modified-since' per-datastore timestamps.
Complete RFC 7895 and RFC 8525 YANG Library support, including full support of the schema retrieval for YANG-API/RESTCONF protocols to retrieve YANG modules from the server and support of server-specific identifier representing the current set of modules and submodules.
Supported Standards
This section provides a summary of the networking standards supported by the netconfd-pro server.
gNMI
This OpenConfig standard defines a network management interface.
This protocol is enabled if gNMI is used
The gNMI protocol is fully supported
gRPC
This OpenConfig standard defines a remote procedure call interface.
RFC 4252 - RFC 4254 Secure Shell
These standards are implemented by the OpenSSH server.
RFC 4252: The Secure Shell (SSH) Authentication Protocol
RFC 4253: The Secure Shell (SSH) Transport Layer Protocol
RFC 4254: The Secure Shell (SSH) Connection Protocol
The netconfd-pro server uses SSH to support NETCONF over SSH sessions. All functionality required by RFC 6242 is implemented.
RFC 4741 NETCONF Base 1.0
This standard provides the first version of the NETCONF protocol, called 'base:1.0'.
RFC 4741: NETCONF Configuration Protocol
This protocol can be disabled by setting the --with-netconf CLI parameter to 'false'.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 4742 NETCONF over SSH v1
This standard provides the first version of the NETCONF over SSH transport.
RFC 4742: Using the NETCONF Configuration Protocol over Secure SHell (SSH)
This protocol version is still in wide use because the framing mechanism does not require that the length of the message in advance.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 5277 NETCONF Notifications
This standard provides the first version of NETCONF Notifications.
RFC 5277: NETCONF Event Notifications
Used for monitoring Event Streams
The <create-subscription> operation is used to start RFC 5277 Subscriptions
Proprietary modules notifications.yang and nc-notifications.yang are defined (since this RFC is before YANG existed)
Notifications can be disabled by setting the --with-notifications CLI parameter to 'false'.
Memory consumption can be reduced using the --eventlog-size CLI parameter.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 5539 NETCONF over TLS
This standard provides the first NETCONF Over TLS protocol mapping.
RFC 5539: NETCONF over Transport Layer Security (TLS)
This protocol must be enabled using the --with-netconf-tls CLI parameter.
Some steps are required to Configure TLS for the client and server.
Several CLI parameters are provided for TLS Configuration
This RFC is fully supported, but now obsoleted by RFC 7589.
RFC 5717 Partial Lock
This standard provides a Database Locking mechanism for locking individual subtrees within the 'running' datastore, instead of the entire datastore.
RFC 5717: Partial Lock Remote Procedure Call (RPC) for NETCONF
Provides the ietf-netconf-partial-lock.yang module
Can only be used if the --target parameter is set to 'running'.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 5789 PATCH Method for HTTP
This standard provides the PATCH method used by the RESTCONF protocol.
RFC 6020 YANG 1.0
This standard provides the first version of the YANG data modeling language. This version is not obsolete, but the RFC 7950 version SHOULD be used instead.
RFC 6020: YANG - A Data Modeling Language for the Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF)
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 6021 YANG Data Types v1
This standard provides the first version of the YANG data types.
RFC 6021: Common YANG Data Types
The module ietf-inet-types.yang is defined
The module ietf-yang-types.yang is defined
This RFC is fully supported, however it has been obsoleted by RFC 6991
RFC 6022 NETCONF Monitoring
This standard provides monitoring information for the server.
RFC 6022: YANG Module for NETCONF Monitoring
The module ietf-netconf-monitoring.yang is defined
The module yuma-time-filter.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf-monitoring' module.
The module yumaworks-system.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf-monitoring' module.
The <get-schema> operation is used to retrieve YANG modules from the server
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 6241 NETCONF base 1.1
This standard defines the current version (called 'base:1.1') of the NETCONF protocol.
RFC 6241: Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF)
Protocol Capabilities are defined
The module ietf-netconf.yang is defined
The module yuma-time-filter.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf' module.
The module yumaworks-system.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf' module.
The module yumaworks-templates.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf' module.
This protocol can be disabled by setting the --with-netconf CLI parameter to 'false'.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 6242 NETCONF over SSH v1.1
This standard provides the current version of the NETCONF over SSH transport.
RFC 6242: Using the NETCONF Protocol over Secure Shell (SSH)
The updated framing mechanism is much better than the 'base:1.0' message framing, and allows a message to be sent in multiple chunks. The server usually sends a chunk when one output buffer is ready.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 6243 With-Defaults
This standard provides mechanisms to retrieve YANG default values from the server.
RFC 6243: With-defaults Capability for NETCONF
Provides the ietf-netconf-with-defaults.yang module
The type of Default Node Handling used is configured with the --default-style CLI parameter
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 6470 Base Notifications
This standard provides standard notification events for the NETCONF event stream.
RFC 6470: Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) Base Notifications
Provides the ietf-netconf-notifications.yang module
The module yumaworks-config-change.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf-notifications' module.
Provides the following standard events:
-
Augmented if the --with-yumaworks-config-change parameter is set to 'true'
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 6536 NACM v1
This standard provides the first version of the NETCONF Access Control model.
RFC 6536: Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) Access Control Model
Provides the ietf-netconf-acm.yang module
This RFC is fully supported, but it is obsoleted by RFC 8341.
RFC 6643 SMIv2 to YANG
This standard provides a translation from SMIv2 MIB modules to YANG syntax.
RFC 6643: Translation of Structure of Management Information Version 2 (SMIv2) MIB Modules to YANG Modules
The translated modules are fully supported
RFC 6991 YANG Data Types v2
This standard provides the second version of the YANG data types.
RFC 6991: Common YANG Data Types
The module ietf-inet-types.yang is defined
The module ietf-yang-types.yang is defined
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 7223 Interface Module v1
This standard provides a YANG module for managing network interfaces. It has been replaced by RFC 8343.
RFC 7223: A YANG Data Model for Interface Management
The module ietf-interfaces.yang is defined.
The 'ietf-interfaces' module is partially supported:
monitoring is fully supported
some configuration parameters are supported
RFC 7224 Interface Types
This standard provides the initial version of the identity definitions for the 'interface-type' data type.
RFC 7230 - RFC 7231 HTTP 1.1
These standards provide the HTTP protocol used by RESTCONF.
RFC 7230: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Message Syntax and Routing
RFC 7231: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content
These RFCs are fully supported by the configured WEB server in the RESTCONF Installation. Many HTTP headers are processed by the RESTCONF server, using the 'FastCGI' programming interface.
RFC 7232 Conditional Requests
This standard provides conditional RESTCONF requests using RESTCONF Headers, which allow a client to optimize data transfers.
RFC 7317 System Module
This standard provides a YANG module for system management.
RFC 7317: A YANG Data Model for System Management
The module iana-crypt-hash.yang is defined.
The module ietf-system.yang is defined.
The 'iana-crypt-hash' module is fully supported:
Loaded automatically by the server
The 'ietf-system' module is partially supported:
Monitoring is partially supported
RPC operations are fully supported
Some configuration parameters are supported
Requires --module='ietf-system' parameter to load
RFC 7407: X.509 Cert to Name
This standard provides configuration parameters for mapping X.509 certificate fields to user names. It is adapted from SNMP to NETCONF.
RFC 7407: A YANG Data Model for SNMP Configuration
The module ietf-x509-cert-to-name.yang is defined.
The module 'ietf-snmp.yang' is defined.
The 'ietf-x509-cert-to-name' module is fully supported
The module yumaworks-cert-usermap.yang uses the 'cert-usermap' grouping to configure mappings at run-time.
The 'ietf-snmp' module is not supported
RFC 7589 NETCONF over TLS v2
This standard provides the current NETCONF Over TLS protocol mapping.
RFC 7589: Using the NETCONF Protocol over Transport Layer Security (TLS) with Mutual X.509 Authentication
This protocol must be enabled using the --with-netconf-tls CLI parameter.
Some steps are required to Configure TLS for the client and server.
Several CLI parameters are provided for TLS Configuration
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 7895 YANG Library v1
This standard provides the first version of the YANG Library. It is used to provide clients with an inventory of the YANG modules used by the server.
RFC 7895: YANG Module Library
The module ietf-yang-library.yang is defined, dated '2016-06-21'.
The new module contains all the contents of this module, but with 'deprecated' status.
The --with-new-yanglib CLI parameter must be set to 'false' to force this module revision to be used.
This RFC is fully supported, but it has been obsoleted by RFC 8525.
RFC 7950 YANG 1.1
This standard provides the current version of the YANG data modeling language.
RFC 7950: The YANG 1.1 Data Modeling Language
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 7951 YANG JSON Encoding
This standard provides JSON encoding of YANG data. This is used by the RESTCONF protocol.
RFC 7951: JSON Encoding of Data Modeled with YANG
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 7952 YANG Metadata
This standard provides definitions for Using YANG Metadata. This is used by the NETCONF protocol.
RFC 7952: Defining and Using Metadata with YANG
The module ietf-yang-metadata.yang is defined
This RFC is partially supported:
The md:annotation extension is fully supported
XML encoding of metadata is fully supported
JSON encoding of metadata is not yet supported
RFC 8040 RESTCONF
This standard defines the RESTCONF protocol.
RFC 8040: RESTCONF Protocol
The RESTCONF Installation must be done to use this protocol.
The ietf-restconf.yang module is defined.
The ietf-restconf-monitoring.yang module is defined.
To disable this protocol, set the --with-restconf CLI parameter to 'false'.
Many RESTCONF Features are supported in addition to this standard.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8071 Call Home
This standard provides the IETF Call Home feature, which allows a server to initiate the transport session to a client.
RFC 8071: NETCONF Call Home and RESTCONF Call Home
There are many Configuration parameters
Runtime configuration is provided with the yumaworks-callhome.yang module.
This RFC is partially supported:
NETCONF Call Home is fully supported
RESTCONF Call Home is not supported
RFC 8072 YANG Patch
This standard defines the YANG Patch mechanism for editing multiple resources at once. It is used by the RESTCONF and High Availability (YP-HA) features.
RFC 8072: YANG Patch Media Type
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8341 NACM v2
This standard provides the current version of the NETCONF Access Control model.
RFC 8341: Network Configuration Access Control Model
Provides the ietf-netconf-acm.yang module
The module yumaworks-system.yang augments the 'ietf-netconf-acm' module.
Applies to RESTCONF and NETCONF
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8342 NMDA
This standard defines the NMDA datastore architecture.
RFC 8342: Network Management Datastore Architecture (NMDA)
The module ietf-datastores.yang is defined
The module ietf-origin.yang is defined
This feature can be enabled by setting the --with-nmda CLI parameter to 'true'.
The 'ietf-origin' module is fully supported
The 'ietf-datastores' module is partially supported:
The conventional datastores are fully supported
The 'operational' datastore is fully supported
The 'intended' datastore is a mirror of the 'running' datastore, and is not fully supported.
RFC 8343 Interface Module v2
This standard provides a YANG module for managing network interfaces.
RFC 8343: A YANG Data Model for Interface Management
The module ietf-interfaces.yang is defined.
The 'ietf-interfaces' module is partially supported:
monitoring is fully supported
some configuration parameters are supported
RFC 8525 YANG Library v2
This standard provides the current version of the YANG Library. It is used to provide clients with an inventory of the YANG modules used by the server.
RFC 8525: YANG Library
The module ietf-yang-library.yang is defined, dated '2019-01-04'.
The subtree '/yang-library' is provided in addition to the older '/modules-state' subtree.
This version is required to use NMDA
The --with-new-yanglib CLI parameter must be set to 'true' (default) to force this module revision to be used.
This module is augmented by ietf-yang-library-augmentedby.yang if the --with-yanglib-augmentedby parameter is set to 'true'.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8526 NETCONF NMDA
This standard provides NETCONF protocol operations for accessing NMDA datastores.
RFC 8526: NETCONF Extensions to Support the Network Management Datastore Architecture
The module ietf-netconf-nmda.yang is defined
The <get-data> and <edit-data> operations are supported.
This module is loaded only if the --with-nmda parameter is set to 'true'.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8527 RESTCONF NMDA
This standard provides RESTCONF protocol operations for accessing NMDA datastores.
RFC 8527: RESTCONF Extensions to Support the Network Management Datastore Architecture
This RFC is partially supported:
Retrieval operations (GET, HEAD) are supported
Edit operations are not supported
The YANG metadata is supported
RFC 8528 Schema Mount
This standard defines the YANG Schema Mount feature.
RFC 8528: YANG Schema Mount
The module ietf-yang-schema-mount.yang is defined
This RFC is partially supported:
The 'ietf-yang-schema-mount' module is fully supported
All RFC features supported except some minor Unsupported Features
RFC 8639 Notification Subscriptions
This standard defines notification Subscriptions for use with NETCONF and RESTCONF. They are called RFC 8639 Subscriptions or 'new' subscriptions.
RFC 8639: Subscription to YANG Notifications
The module ietf-subscribed-notifications.yang is defined
This RFC is partially supported:
A few optional YANG features are not supported
Dynamic subscriptions are fully supported
Configured Subscriptions are fully supported if YANG Push 2 is used
RFC 8640 NETCONF Subscriptions
This standard defines requirements for using RFC 8639 with the NETCONF protocol.
RFC 8640: Dynamic Subscription to YANG Events and Datastores over NETCONF
This RFC is partially supported:
All mandatory functionality is supported
All event stream and YANG Push functionality is fully supported
Error info fields using specified error identities are not supported
RFC 8641 YANG Push
This standard defines notifications to YANG datastores. It is called YANG Push.
RFC 8641: Subscription to YANG Notifications for Datastore Updates
The module ietf-yang-push.yang is defined
The YANG Push 2 feature adds several YANG modules that require the 'ietf-yang-push' module. These modules are under development and not finalized yet:
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8650 RESTCONF Subscriptions
This standard defines requirements for using RFC 8639 with the RESTCONF protocol. RESTCONF Subscriptions use the <establish-subscription> operation similar to NETCONF, except a URI is returned to use for retrieval.
RFC 8650: Dynamic Subscription to YANG Events and Datastores over RESTCONF
The module ietf-restconf-subscribed-notifications.yang is defined
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8791 YANG Structures
This standard defines YANG extensions that allow abstract structures to be defined and augmented. These structures are often used to model artifacts and protocol messages. Regular YANG data nodes are included in datastores, but not YANG structures.
RFC 8791: Support for Structure and Augment-Structure YANG Extension Statements
The module ietf-yang-structure-ext.yang is defined
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8808 Factory Default
This standard defines the factory default datastore support.
RFC 8808: A YANG Data Model for Factory Default Settings
The module ietf-factory-default.yang is defined
The --with-factory-datastore parameter must be set to 'true' for this module to be loaded.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 8949 CBOR
This standard defines the binary data encoding used by RFC 9254.
RFC 8949: Concise Binary Object Representation (CBOR)
This encoding is only used if Binary Push is used.
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 9196 Notification Capabilities
This standard defines a YANG module for monitoring the notification capabilities of the server.
RFC 9196: YANG Modules Describing Capabilities for Systems and Datastore Update Notifications
The module ietf-system-capabilities.yang is defined
The module ietf-notification-capabilities.yang is defined
The 'ietf-system-capabilities' module is partially supported:
global capabilities are supported
per-node capabilities are not supported
The 'ietf-notification-capabilities' module is fully supported.
RFC 9254 YANG CBOR
This standard defines CBOR encoding of YANG instance data.
RFC 9254: Encoding of Data Modeled with YANG in the Concise Binary Object Representation (CBOR)
The CBOR encoding is used by the Binary Push feature
This RFC is fully supported
RFC 9595 YANG SID Files
This standard defines mechanisms for managing and defining YANG SID files.
RFC 9595: YANG Schema Item iDentifier (YANG SID)
The module ietf-sid-file.yang is defined
YANG SID files are used by the Binary Push feature
This RFC is fully supported
XML 1.0
This standard defines the XML encoding used by the NETCONF and RESTCONF protocols.
XML encoding is fully supported
XPath
This standard defines the XML Path language used in YANG and NETCONF XPath filtering.
The XPath 1.0 standard is fully supported
All extensions required by RFC 7950 are fully supported
Server Programs
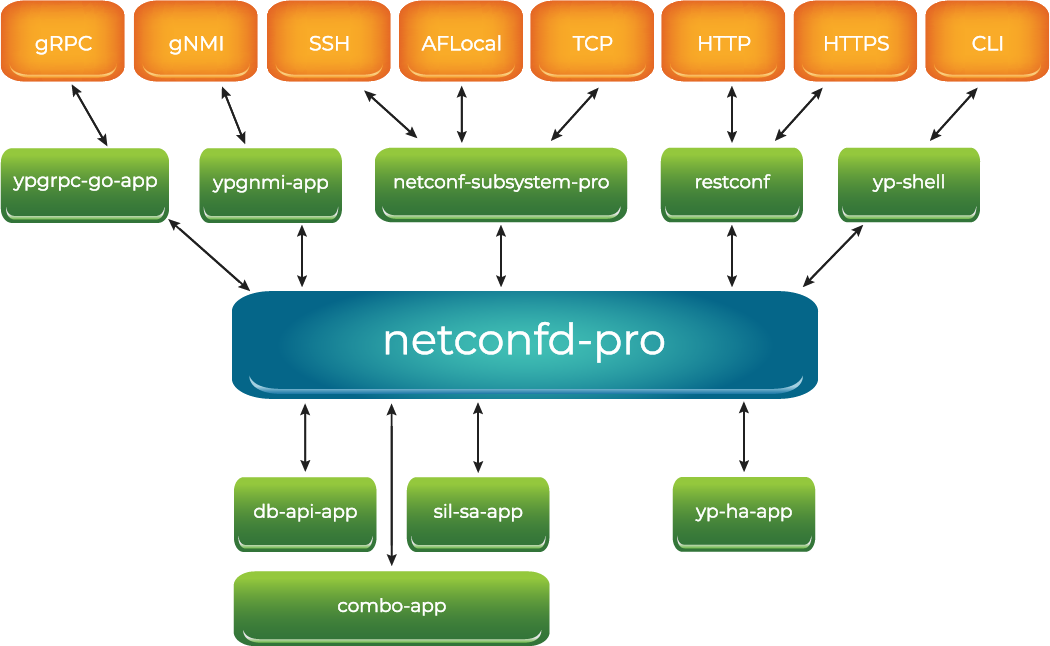
The server can be deployed in many different ways. In every case, the 'netconfd-pro' program is used. Depending on the protocols used and the deployment choices, there will be additional programs used.
The server programs have been moved to the YumaPro Programs section. They are just listed here.
Setting the Server Profile
The netconfd-pro server can behave in different ways, depending on the initial configuration parameters used.
The following parameters should be considered, and if the default behavior is not desired, then an explicit value should be provided instead:
--yumapro-home or $YUMAPRO_HOME setting will affect YANG search path.
--modpath or $YUMAPRO_MODPATH setting will affect YANG search path.
--loadpath or $YUMAPRO_LOADPATH setting will affect YANG module load path.
--datapath or $YUMAPRO_DATAPATH setting will affect startup-cfg.xml search path.
--target setting will select the edit target. The default is 'candidate', so this parameter must be set to choose 'running' as the edit target.
--with-startup setting will enable the <startup> database if set to 'true'.
--with-validate setting will enable the :validate capability if set to 'true'
--access-control setting will affect how access control is enforced. The default is fully on ('enforcing').
--superuser setting will affect access control, if it is enabled. The default is no superuser.
--default-style setting will affect how default leaf values are returned in retrieval requests. The default is 'trim'. This returns everything except leafs containing the YANG default-stmt value, by default. To report every leaf value by default, set this parameter to 'report-all'. To report only leafs not set by the server by default, use the 'explicit' enumeration.
--log, --log-level, and --log-pthread-level settings will affect what log messages are generated. The default is to send all messages to STDOUT, and use the 'info' logging level.
--log-stderr, --log-syslog, --log-syslog-level, --log-header, --log-console, and several other log related commands will also affect how log messages are generated. A detailed discussion on the action of the various logging related parameters is included in the YumaPro User Manual. All available commands are also documented in the :YumaPro CLI Reference section.
--eventlog-size setting will control the memory used by the notification replay buffer
--max-burst will control the of notifications sent at once to a single session
--hello-timeout will control how long sessions can be stuck waiting for a hello message before they are dropped.
--max-sessions will limit the number of concurrent sessions allowed
--max-cli-sessions will limit the number of concurrent CLI (yp-shell) sessions allowed
--idle-timeout will control how long active sessions can remain idle before they are dropped.
--subsys-timeout will control how long the server will wait for replies from a subsystem.
Loading YANG Modules
Loading Modules at Boot-Time
The --module parameter can be used from the CLI or .conf file to pre-load YANG modules and any related device instrumentation code into the server. A fatal error will occur if any module cannot be loaded, or it contains any YANG errors.
The --loadpath parameter can also be used to specify a sequence of directories to check for YANG modules. Any modules found in the path that have not already been loaded with --module or --bundle parameters will be loaded into the server.
Loading Modules at Run-Time
At run-time, the <load> operation (defined in yuma-system.yang and yumaworks-system.yang) can be used to load a YANG module. The server will return an <rpc-error> if the requested module cannot be loaded. By default, only a superuser can invoke the <load> operation. If the <save-config> parameter is set to 'true' then a module configuration file will be saved so the module will be loaded after a reboot.
Loading Bundles at Boot-Time
The --bundle parameter can be used to load a collection of YANG modules and the SIL code for those modules. It cannot be used to load a single YANG module without any SIL code available to the server. The make_sil_bundle script is used to create the C callback functions for all YANG modules in the SIL bundle. SIL code for all “external augments” data is also generated when a SIL bundle is created.
Loading Bundles at Run-Time
At run-time, the <load-bundle> operation (defined in yumaworks-system.yang) can be used to load a SIL bundle (SIL code + all YANG modules in the bundle). The server will return an <rpc-error> if the requested SIL bundle cannot be loaded. By default, only a superuser can invoke the <load-bundle> operation. If the <save-config> parameter is set to 'true' then a module configuration file will be saved so the bundle will be loaded after a reboot.
All modules imported by the explicitly specified modules will also be loaded.
leaf save-config {
type boolean;
default false;
description
"If 'true' then save the module or bundle load
configuration in the --confdir directory, if the
load or load-bundle operation is completed without
errors.
Ignored if the --no-config CLI parameter is used
or the --confdir CLI parameter is not specified
and no default configuration directory is found.
A configuration file is created or replaced in this
directory with the name <module-name>.conf.";
}
Unloading YANG Modules
Any module that was loaded with the --module parameter or <load> operation can be unloaded with the <unload> operation. By default, only a superuser can invoke the <unload> operation. If the <delete-config> parameter is set to 'true' then the module configuration file will be deleted so the module will not be loaded after a reboot.
Modules imported by the module being unloaded are not unloaded.
Modules loaded as a bundle with the --bundle parameter can be unloaded with the <unload-bundle> operation. By default, only a superuser can invoke the <unload-bundle> operation. If the <delete-config> parameter is set to 'true' then the module configuration file will be deleted so the bundle will not be loaded after a reboot.
Modules imported by the bundle are unloaded.
If any modules not being removed are importing the module(s) being unloaded, then the operation will fail and an <rpc-error> will be returned.
leaf delete-config {
type boolean;
default false;
description
"If 'true' then delete the module or bundle load
configuration in the --confdir directory, if the unload
or unload-bundle operation is completed without errors.
Ignored if the --no-config CLI parameter is used
or the --confdir CLI parameter is not specified
and no default configuration directory is found.
A configuration file is deleted in this
directory with the name <module-name>.conf.";
}
Starting netconfd-pro
The current working directory in use when netconfd-pro is invoked is important. It is most convenient to run netconfd-pro in the background, and save all output to a log file.
The netconfd-pro program listens for connection requests on a local
socket, that is located in /tmp/ncxserver.sock.
In order for NETCONF sessions to be enabled, the SSH server and the netconf-subsystem-pro programs must be properly installed first.
The netconfd-pro program does not directly process the SSH protocol messages. Instead, it is implemented as an SSH subsystem. The number of concurrent SSH sessions that can connect to the netconfd-pro server at once may be limited by the SSH server configuration. Refer to the YumaPro Installation Guide for more details on configuring the SSH server for use with netconfd-pro.
Starting netconfd-pro Examples
The netconfd-pro program can be invoked several ways:
To get the current version and exit:
netconfd-pro --version
To get program help and exit:
netconfd-pro --help
netconfd-pro --help --brief
netconfd-pro --help --full
To start the server in the background, set the logging level to 'debug', and send logging messages to a log file
netconfd-pro --log-level=debug --log=~/mylog &
To start the server interactively, and send all log messages to STDOUT:
netconfd-pro
To start the server interactively, with a new log file:
netconfd-pro --log=mylogfile
To start the server interactively, and append to an existing log file:
netconfd-pro --log=mylogfile --log-append
To get parameters from a non-default configuration file:
netconfd-pro --config=/opt/conf/netconfd-pro.conf
To run as root and use the FHS file locations:
netconfd-pro --fileloc-fhs=true
Starting netconfd-pro With A Log File
The netconfd-pro program is usually started at system boot time. The main logging output is usually sent to a log file, or 'syslog', or both.
If no logging parameters are specified, then the default is to set the main logging output to 'stdout', and the --log-level to 'info'.
Copyright Notices
The logging output includes copyright messages that cannot be removed from the program.
Example: starting netconfd-pro with all default parameters:
andy@andy-i9-homedev:~$ netconfd-pro
Starting netconfd-pro...
Copyright (c) 2008-2012, Andy Bierman, All Rights Reserved.
Copyright (c) 2012-2023, YumaWorks, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
Note
The startup banner will be displayed to 'stdout' if logging parameters are provided in the config file.
Put logging parameters on the command line to avoid any copyright output to 'stdout'.
Provide the following logging parameters on the command line to avoid any output to 'stdout' when the program starts.
Example:
> netconfd-pro --log=/home/user/test1.log
Starting SIL-SA Subsystems with sil-sa-app
If the server is built using the WITH_YCONTROL=1 or EVERYTHING=1 make flag then it will listen for "sil-sa" service connections from SIL-SA subsystems. The sil-sa-app program can be used to support the SIL-SA libraries on a subsystem.
A subsystem can run on the same system as netconfd-pro or a different system.
A subsystem can be started before or after the main server. Connect and re-connect functionality is built into the program.
The following sil-sa-app CLI parameters are supported:
--address=ip-address
The IP address of the main server.
The default is to use the server on the same system as the sil-sa-app process.
If this parameter is used, then netconfd-pro must set the --socket-type parameter to 'tcp'.
If netconfd-pro uses the --socket-address parameter, then this parameter must match its value.
--library=string
The --library parameter keyword is optional. It specifies a SIL-SA library (module or bundle) that should be selected by this subsystem.
If any --library parameters are present, then only those SIL-SA libraries will be loaded by this subsystem, if the main server indicates that the module or bundle is loaded.
If no --library parameters are present then the sil-sa-app will attempt to load all SIL-SA modules and bundles reported by the server.
Example:
# select libfoo_sa.so --library=foo
--log-level=enum
The output log level to use. The default is ‘info’.
--log=filespec
The output log file to use. The default is ‘stdout’
--port=uint16
The TCP port number to use, Ignored unless address is also present.
The default is 2023.
If this parameter is used, then netconfd-pro must use the --socket-type=tcp parameter.
If netconfd-pro uses the --socket-port parameter, then this parameter must match its value.
--subsys-id=string
The subsystem identifier to use.
The default is
subsys1.This value must be unique among all the subsystems registered on the same server.
The SIL-SA libraries loaded depends on 2 factors:
The <module> and <bundle> parameters included in the <register-response> message from the server. The sil-sa-app program will attempt to find the SIL-SA libraries for these modules and bundles.
The program will look in the
/usr/lib/yumaprodirectory. If a library is not found, then the module will be skipped The SIL-SA libraries supported on a subsystem can be controlled by limiting which SIL-SA libraries are present.
Example: Start the server with a non-default socket
# server started
> netconfd-pro --socket-type=tcp --socket-address=192.168.0.45 --socket-port=8090
# sil-sa-app started
> sil-sa-app --subsys-id=sub1 --address=192.168.0.45 --port=8090
Example 2: Start 2 subsystems on the same host
# server started
> netconfd-pro --module=mod1 --module=mod2
# sil-sa-app started
> sil-sa-app --subsys-id=sub1 --library=mod1
> sil-sa-app --subsys-id=sub2 --library=mod2
Starting SIL-SA Subsystems with py-sil-app
For more details on how to use py-sil-app refer to Starting PY-SIL Subsystems with py-sil-app
Stopping netconfd-pro
To terminate the netconfd-pro program when running interactively, use the control-C character sequence. This will cause the server to cleanup and terminate gracefully.
The <shutdown> or <restart> operations can also be used to terminate or restart the server. The ietf-netconf-acm.yang access control rules must be configured to allow any user except the 'superuser' account to invoke this operation.
Signal Handling
The server will respond to Unix signals sent to the netconfd-pro process.
If the server is being run in the foreground, then the Control-C character sequence will perform the same action as a SIGINT signal.
Signals Recognized by netconfd-pro
Signal |
Number |
Description |
SIGHUP (Hangup) |
1 |
Restart the server. |
SIGINT (Control-C) |
2 |
Shutdown the server. |
SIGQUIT |
3 |
Shutdown the server. |
SIGILL |
4 |
Shutdown the server. |
SIGTRAP |
5 |
Shutdown the server. |
SIGABRT |
6 |
Shutdown the server. |
SIGKILL |
9 |
Kill the server process (No proper cleanup!) |
SIGUSR1 |
10 |
Reload the server (Does a restart) |
SIGUSR2 |
12 |
Logrotate (reopen log files) |
SIGPIPE |
13 |
Handle I/O connection error. |
SIGTERM |
15 |
Shutdown the server. |
SIGVTALRM |
26 |
Internal threads kill signal |
The kill command in Unix can be used to send signals to a process running in the background. In order to shutdown the server properly with the kill command, use “kill -TERM” not “kill -9”. Refer to the Unix man pages for more details.
Example to shutdown the server with "kill -TERM":
# Get the PID of the server
> ps aux | grep netconfd-pro
user1 14166 0.1 0.0 163852 15616 pts/2 S+ 19:10 0:00 netconfd-pro
# the first number is the PID
> kill -TERM 14166
Starting netconfd-pro with ypwatcher program
The ypwatcher is a program that provides monitoring mechanism to netconfd-pro server and its state. Ypwatcher Ypwatcher program periodically checks the server's state and determine if the server is still running. If the server is no longer running it cleans up the state, restarts the server, and generates a syslog message.
The ypwatcher program will be launched by the server by default unless --no-watcher parameter will be specified or the program is already running.
The ypwatcher program is running continuously and attempting to restart the server any time it exits unexpectedly.
The ypwatcher program will be invoked automatically whether the server starts interactively or in the background mode:
To start the server interactively, with the ypwatcher program:
netconfd-pro
To start the server interactively, with no ypwatcher program:
netconfd-pro --no-watcher
The --watcher-interval parameter specifies the sleep interval between ypwatcher program attempts to check availability of the server.
To start the server interactively, with ypwatcher program and set the watcher interval:
netconfd-pro --watcher-interval=10
Signal Handling with ypwatcher program
The ypwatcher program is running continuously and attempting to restart the server any time it exits unexpectedly.
Unexpected exit can be interpreted as a server's shut down process due to severe error, such as Segmentation fault, core dump, bus error, and invalid memory reference. The ypwatcher program will restart the server only if any of these termination actions causing the server to shut down.
During the RESTART and RELOAD operations the netconfd-pro and ypwatcher remains the same state and PID numbers.
With ypwatcher the server will still respond to Unix signals sent to the netconfd-pro process.
If the server is being run in the foreground, then the Control-C character sequence will perform the same action as a SIGINT signal and ypwatcher program will terminate as well.
The ypwatcher program will restart the server that shutdown because of the following signals:
Signals Recognized by ypwatcher
Signal |
Number |
Description |
SIGBUS |
7 |
Bus error. |
SIGFPE |
8 |
Floating Point exception. |
SIGKILL |
9 |
Kill |
SIGSEGV |
11 |
Invalid memory reference |
The :kill command in Unix can be used to send signals to a process running in the background. Refer to the Unix man pages for more details.
netconfd-pro Error Handling
All of the error handling requirements specified by the NETCONF protocol, and the YANG language error extensions for NETCONF, are supported automatically by netconfd-pro.
The following CLI parameters affect error handling:
--errmsg : change the error-message for a specific error and language
--errmsg-lang : change the error-message language
--running-error : change boot-up error handling for <running> datastore
--startup-error : change boot-up error handling for loading startup configuration
Refer to the Error Reporting CLI Parameters section for the complete list of CLI parameters that affect error handling and error reporting.
There are 4 categories of error handling done by the server:
Incoming PDU validation
Errors for invalid PDU contents are reported immediately. The server will attempt to find all the errors in the input <rpc> request, and not stop detecting errors after one is found.
All machine-readable YANG statements are utilized to automate the detection and reporting of errors.
A node that is present, but has a false 'when' statement, is treated as an error.
Server instrumentation PDU validation
Semantic requirements expressed only in description statements will be checked by device instrumentation callbacks. The specific YANG data module should indicate which errors may be reported, and when they should be reported.
Database validation
Several automated tests are performed when a database is validated.
If the edit target is the <candidate> configuration, then referential integrity tests are postponed until the <commit> operation is attempted.
The specific conditions checked automatically are:
referential integrity condition test failed (must)
missing leaf (mandatory)
missing choice (mandatory)
extra container or leaf
too few instances of a list or leaf-list (min-elements)
too many instances of a list or leaf-list (max-elements)
instance not unique (unique)
Nodes that are unsupported by the server will automatically be removed from these tests. This can occur in the following ways:
node is defined within a feature that is not supported (if-feature)
node has conditional existence test that is false (when)
nodes derived from a 'uses' statement which has a conditional existence test that is false (when)
nodes derived from an 'augment' statement which has a conditional existence test that is false (when)
Server instrumentation database validation and activation
Errors can occur related to the specific YANG data model module, which can only be detected and reported by the server instrumentation.
Resource denied errors can occur while the server instrumentation is attempting to activate the networking features associated with some configuration parameters.
Instrumentation code can fail for a number of reasons, such as underlying hardware failure or removal.
Module Summary
The following YANG modules are built into the netconfd-pro server, and cannot be loaded manually with the --module parameter or <load> operation. YumaWorks modules can be disabled with various CLI parameters.
Pre-loaded YANG Modules
Module |
Description |
|---|---|
IANA crypt-hash data type |
|
NMDA datastore meta-data |
|
Message Publisher ID support for YANG Push 2 |
|
Contains Factory Default Support |
|
Standard data types |
|
Standard NETCONF access control model |
|
Standard NETCONF monitoring, and the <get-schema> operation |
|
NMDA operations for NETCONF, including <get-data> |
|
Standard NETCONF notifications for system events |
|
Standard NETCONF <partial-lock> and <partial-unlock> operations |
|
<with-defaults> extension |
|
NMDA <operational> origin meta-data |
|
YANG SID File support for Binary Push |
|
Notification Receiver groupings for UDP-Notif Protocol |
|
Dynamic Notification Subscriptions from RFC 8639 |
|
System Capabilities Monitoring |
|
UDP Receiver groupings for Configured Subscriptions |
|
Main module for UDP-Notif Protocol |
|
X.509 cert-to-name configuration used for NETCONF over TLS |
|
Standard NETCONF YANG Module Library that represents the current set of modules and submodules. |
|
Augments the YANG Library with the 'augmented-by' leaf-list |
|
Standard YANG Module containing the md:annotation extension. |
|
Subscriptions to YANG Datastores from RFC 8641 |
|
Required Module Revisions for notification subscriptions |
|
YANG Schema Mount from RFC 8528 |
|
Standard data types |
|
Standard replay notifications |
|
Server CLI parameters |
|
Standard notification operations |
|
openconfig-extensions.yang |
Many OC extensions supported (used in other modules) |
Yuma NETCONF extensions |
|
Common CLI parameters |
|
Yuma common data types |
|
Get and Set session-specific parameters |
|
System monitoring, operations, and notifications. This module is deprecated. It is enabled by default, but can be removed using --with-yuma-system=false |
|
Get only if datastore changed since a specified timestamp |
|
Common definitions used by yumapro modules |
|
Extensions to add last-modified and etag attributes |
|
Runtime configuration of Call Home server parameters |
|
Add X.509 cert-to-name mapping configuration used for NETCONF over TLS |
|
NETCONF <compare-config> operation to compare configurations |
|
Add edit data to the netconf-config-change notification |
|
Event filters to suppress generation of notifications for the specified events |
|
NETCONF Event stream configuration |
|
YANG extensions for meta-data data tagging |
|
NETCONF <get-bulk> operation to easily iterate through YANG lists |
|
Session type extensions for the standard monitoring module |
|
NETCONF <lock-all> and <unlock-all> operations to simplify datastore locking for editing |
|
Extensions to add confirmed-commit procedure to RESTCONF |
|
Deviations for ietf-subscribed-notifications.yang to identify currently unimplemented portions |
|
Contains the sm-config Structure for Schema Mount configuration |
|
Contains the <get-sm-yanglib> operation to retrieve Schema Mount YANG libray information |
|
Contains the <get-support-save> operation |
|
Extensions to ietf-netconf-monitoring, plus extra protocol operations for backup/restore, unload, etc. |
|
YANG System deviations to identify currently unimplemented portions |
|
<term-msg> Notification for yp-shell diagnostic messages |
|
YANG Push deviations to identify currently unimplemented portions |
The following YANG modules are not built into the netconfd-pro server, but if specific build variable is set during the build, netconfd-pro will activate corresponding modules.
Optional YANG Modules
Module |
Description |
Status |
|---|---|---|
Monitoring information for the RESTCONF protocol. Build variable: WITH_RESTCONF=1 |
current |
|
collection of YANG definitions for configuring and monitoring ARP. Build variable: WITH_YUMA_ARP=1 |
obsolete |
|
NETCONF /proc file system monitoring. Build variable: WITH_YUMA_PROC=1: |
obsolete |
|
Yuma interfaces table. Build variable: WITH_YUMA_INTERFACES=1. |
obsolete |
|
Contains the sm-config Structure for Schema Mount configuration. Build variable: WITH_SCHEMA_MOUNT=1: |
current |
|
Allows server CLI parameters to be edited at run-time |
current |
|
Allows client to retrieve Binary Push configuration. Build variables: WITH_YANG_CBOR=1 and WITH_YANG_PUSH=1. |
current |
Notification Summary
There are some CLI parameters that affect notifications that need to be set (or default value used):
CLI Parameters for Notifications
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Size of the replay buffer for the NETCONF event stream |
|
Configure a notification event stream |
|
Configure a module to event stream mapping |
|
Has no affect if notification delivery is active |
|
Report dropped notifications in the server log |
|
Control number of notifications sent at once to a receiver |
|
Control size of message chunks sent to the receiver |
|
Pick IETF or Yuma system notifications. Default is IETF. Yuma is deprecated and should not be used |
|
Must be set to true to enable notification delivery |
|
Must be set to true to enable <term-msg> event |
|
Must be set to true if --system-notifications set to include yuma |
The following notification event types are built into the netconfd-pro server:
Pre-loaded Notifications for :RFC:`5277` and :RFC:`7895`
Module |
Event Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
nc-notifications |
Notification replay has ended |
|
nc-notifications |
Notification delivery has ended |
|
ietf-yang-library |
Set of modules or submodules in the YANG Library has changed |
Pre-loaded Notifications if system-notifications includes “ietf” (Default)
Module |
Event Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ietf-netconf-notifications |
NETCONF session has started |
|
ietf-netconf-notifications |
NETCONF session has ended |
|
ietf-netconf-notifications |
<running> configuration has changed |
|
ietf-netconf-notifications |
Server capabilities have changed |
|
ietf-netconf-notifications |
Confirmed commit procedure event |
Pre-loaded Notifications if system-notifications includes “yuma” (Deprecated)
Module |
Event Type |
Description |
yuma-system |
<sysStartup> |
server startup event |
yuma-system |
<sysSessionStart> |
NETCONF session has started |
yuma-system |
<sysSessionEnd> |
NETCONF session has ended |
yuma-system |
<sysConfigChange> |
<running> configuration has changed |
yuma-system |
<sysCapabilityChange> |
Server capabilities have changed |
yuma-system |
<sysConfirmedCommit> |
Confirmed commit procedure event |
Pre-loaded Notifications if yang-push bundle enabled
Module |
Event Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
ietf-subscribed-notifications |
subscription replay complete |
|
ietf-subscribed-notifications |
subscription configuration modified |
|
ietf-subscribed-notifications |
configured subscription started or reset |
|
ietf-subscribed-notifications |
subscription terminated |
|
ietf-yang-push |
YANG Push Complete Update |
|
ietf-yang-push |
YANG Push Patch Update |
Operation Summary
The following protocol operations are built into the netconfd-pro server. Some built-in modules need to be enabled to be present, but the code may be present in the server image.
Pre-loaded Operations
Module |
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|---|
none |
Invoke a YANG 1.1 action defined in RFC 7950 Section 7.15 |
|
Backup the running configuration to a file |
||
Cancel a confirmed-commit operation |
||
Cancel a notification subscription |
||
Clear the replay buffer for an event stream |
||
Terminate the current session |
||
Activate edits in <candidate> |
||
Compare configurations |
||
Copy an entire configuration |
||
Start receiving notifications |
||
Delete a backup configuration file |
||
Delete a configuration |
||
Delete a notification subscription by the owner session |
||
Discard edits in <candidate> |
||
Edit the target configuration datastore |
||
Edit the target configuration datastore |
||
Start a notification subscription |
||
Start a full factory reset |
||
Retrieve <running> or state data |
||
Retrieve all or part of a configuration |
||
Retrieve data from an NMDA datastore |
||
Retrieve N list entries at a time |
||
Retrieve YP-HA status information |
||
Retrieve the installed module-tags |
||
Retrieve session customization parameters |
||
Retrieve a YANG or YIN module definition file |
||
Retrieve the server version and build-date |
||
Retrieve the Schema Mount YANG Library information |
||
Terminate a NETCONF session |
||
Delete a notification subscription by any session |
||
Load a YANG module and its SIL code [DEPRECATED] |
||
Load a YANG module and its SIL code |
||
Load a SIL bundle (SIL code + modules |
||
Internal RPC to load <running> datastore at boot-time |
||
Lock a database |
||
Lock all configuration databases at once |
||
Modify a notification subscription |
||
No operation. [DEPRECATED] |
||
Lock part of the <running> database |
||
ietf-netconf-partial-lock |
Unlock part of the <running> database |
|
Enable or disable client protocol sessions |
||
Refresh the backup-files monitoring data |
||
Internal RPC operation for configuration datastore synchronization |
||
Update the NETCONF over TLS server certificate and key at run-time |
||
Restart the server. [DEPRECATED] |
||
Restore the <running> database from a backup |
||
Re-synchronize a YANG Push notification subscription |
||
Set the logging verbosity level [DEPRECATED] |
||
Set the logging verbosity level |
||
Set the session customization parameters |
||
Shutdown the server [DEPRECATED] |
||
Unload a YANG module and its SIL code |
||
Unload a SIL bundle, and all its YANG modules and SIL code |
||
Unlock a database |
||
Unlock all configuration databases at once |
||
Validate a database |
netconfd-pro Configuration Parameter List
The following configuration parameters are used by netconfd-pro. Refer to the YumaPro CLI Reference for more details.
netconfd-pro CLI Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
Specifies how access control will be enforced |
|
Allow delete-all operations on leaf-list objects |
|
Allow delete-all operations on list objects |
|
Limits sessions to specified user names |
|
Specifies whether the server will recognize the 'alt-name' YANG extension which allows an alternate name to be used for a node in the database.` |
|
Specifies a YANG module to load as an annotations module |
|
Specifies the audit log of changes to the running database, after initial load is done. |
|
Specifies that no default audit log should be created when --fileloc-fhs is set to ‘true’ |
|
Append audit entries to the existing log if present; Otherwise start a new audit log. |
|
Record transactions on the candidate datastore or not |
|
Minimum debug level to generate console audit log messages |
|
Select which events are recorded in the audit log |
|
Minimum debug level to generate audit log messages |
|
Modify the audit log to include timestamps in the local time zone |
|
Treat false when-stmts in the edit PDU as errors |
|
Maximum number of bytes o display of binary data for a YANG object |
|
Specifies a SIL bundle to load into the server at boot-time |
|
Specifies whether server will reconnect after client closes the session |
|
Specifies the number of seconds to wait after a connect attempt to the Call Home server has failed before attempting another connect attempt to that server. |
|
Specifies the number of retry attempts the server should attempt to the Call Home server before giving up. |
|
Specifies a NETCONF over SSH Call Home server that this server should attempt to initiate a Call Home connection at boot-time. |
|
Specifies the command used in Call Home to invoke the SSH server |
|
Specifies the filespec for the config file used in Call Home to invoke the SSH server |
|
Specifies the command used in Call Home to invoke the netconf subsystem |
|
Specifies a NETCONF over TLS Call Home server |
|
Specifies the default user name to certificate mapping (DEBUG only) |
|
Specifies a user-name to certificate mapping |
|
Specifies the directory for extra configuration parameter files |
|
Specifies the configuration file to use for parameters |
|
Convert subtree filters to XPath for internal processing |
|
Specifies that empty NP containers should be created or not |
|
Specifies that empty NP containers with read-only children should be created or not |
|
Specifies the search path for the <startup> configuration file. |
|
Specifies the amount of time to wait before retrying a DB-Config-Lock |
|
Specifies the amount of time to wait before giving up attempting to get a DB-Config-Lock |
|
Specifies the default <with-defaults> behavior |
|
Specifies that empty NP containers should be deleted or not (THIS PARAMETER IS OBSOLETE) |
|
Species a YANG module to load as a deviations module |
|
Do not add top-level data nodes from imported modules |
|
Disabled client protocols ready to enable at run-time |
|
Specifies a language-specific error message |
|
Specifies the error-message language to use |
|
Specifies the maximum number of events stored in the notification replay buffer. |
|
Configure a notification event stream |
|
Configure a module to event stream mapping |
|
Force the startup and running datastores to contain the factory startup configuration |
|
Leaf list of features to disable |
|
Specifies a feature that should be enabled |
|
Specifies if a feature should be enabled or disabled by default |
|
Selects Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) directory locations |
|
Enable or disable the YP-HA feature |
|
Set the YP-HA active server to use at boot-time (for debugging only) |
|
Specify a server to be a member of the YP-HA server pool |
|
Unique string identifying the YP-HA server pool |
|
Enable edit callbacks (SIL, etc.) while in YP-HA Standby mode |
|
Set the number of seconds to wait for a <hello> PDU |
|
Get context-sensitive help with --brief or --full extension |
|
Hide the specified module from clients |
|
Include a microseconds field in the notification 'eventTime' leaf |
|
Overrides the $HOME environment variable |
|
Set the number of seconds to wait for a <rpc> PDU |
|
Enable import version best match feature |
|
Specifies the indent count to use when writing data |
|
Specifies if unverified client certificates will be accepted (DEBUG only) |
|
Run the server in YANG library mode |
|
Sets the module load path |
|
Specifies the log file to use instead of STDOUT. Refer to the Logging section for more details. |
|
Controls whether a log file will be reused or overwritten. |
|
Append stack trace information to log messages. |
|
Add additional (compiler/OS dependent) detail to stack trace information. |
|
Specify message level(s) for which stack trace information will be generated. |
|
Include stack trace information in the specified output stream(s) |
|
Specifies that log output will be sent to STDOUT after being sent to log file and/or syslog (assumes the presence of --log and/or --log-syslog/--log-vendor). |
|
Indicates if log entry would be generated when a notification is dropped because the specific notification events are disabled with an event-filter configuration entry.` |
|
Include additional information (date/time/level) with log message. |
|
Include a microseconds field in the log timestamps. |
|
Specifies verbosity level of log message output |
|
Synonym for --log-console. |
|
Specifies verbosity level of thread-specific log message output. Not active in non-threaded images. |
|
Specifies that error level log messages will be sent to STDERR. |
|
Send log message output to the syslog daemon. |
|
Specifies filter level for syslog message output. Message levels above the specified level are filtered from the syslog or vendor output stream. |
|
Directs log output to a registered, customer-written callback handler. Uses syslog if no handler is registered. |
|
Specifies how names are matched when performing UrlPath searches. |
|
Specifies the maximum number of notifications to send at once |
|
Control size of message chunks sent to the receiver |
|
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent CLI sessions allowed |
|
Specifies the maximum number of getbulk entries to request from a GET2 callback. |
|
Specifies the maximum number of seconds a session can hold a global lock |
|
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent sessions allowed for one user |
|
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent sessions allowed |
|
Specifies tha maximum length of a quoted string to accept by the parser |
|
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent sessions allowed for all users |
|
Specifies the amount to indent in protocol messages |
|
Sets the module search path |
|
Specifies one or more YANG modules to load upon startup |
|
Specifies a module name to module-tag mapping |
|
Specifies a NETCONF capability URI to add to the server |
|
Specifies the IP address to listen for NETCONF over TLS sessions |
|
Specifies the X.509 certificate to use for NETCONF over TLS |
|
Specifies the X.509 private key to use for NETCONF over TLS |
|
Specifies the TCP port to list for NETCONF over TLS sessions |
|
Specifies the trust store file or directory for NETCONF over TLS |
|
If present, ignore the default configuration file |
|
Suppress the main log and set --log-level=none |
|
Disable internal NV-load and NV-store operations |
|
If present, the startup configuration will not be used (if present), and the factory defaults will be used instead. |
|
Disable the ypwatcher program |
|
Specifies up to 4 TCP port numbers to accept NETCONF connections from |
|
Specifies which NETCONF protocol versions to enable |
|
Specifies the maximum number of on-change push subscriptions |
|
Specifies the maximum number of periodic push subscriptions |
|
Specifies the minimum value for the 'dampening-period' parameter |
|
Specifies the minimum value for the 'period' parameter |
|
Specifies if the simulated on-change push subscriptions should be enabled |
|
Specifies the simulated on-change push subscription report type |
|
Specifies the period that will be used for simulated operational on-change push subscription |
|
Specifies whether deprecated leafs from a yumaworks-system.yang augmentation will be removed or not. |
|
Specifies a RESTCONF capability URI to add to the server |
|
Specifies the default response message encoding for RESTCONF |
|
Specifies the starting string for the server URL to use in Location header lines returned by RESTCONF. |
|
Specifies how the RESTCONF server will validate Accept and Content type headers |
|
Specifies that empty NP containers should be returned or not |
|
Controls whether "<rpc-error>" nodes will be returned in RPC output for retrieval operations |
|
Specifies how the server will return a status code upon exit |
|
Server instrumentation library (SIL) search path |
|
Specifies whether the server should stop, continue, or fallback to factory default if the running configuration contains any errors at boot-time (such as missing mandatory nodes) |
|
Specifies whether owner names will be saved as meta-data in the configuration data |
|
String identifying the server in the YP-HA server pool |
|
String identifying the server root when running in Multi-Instance Mode |
|
If present, will force synchronous request processing (pthread version only) |
|
Specifies that the CC callbacks should be invoked for all edit operations. (See Using Commit Completeness Callbacks) |
|
Specifies that the SIL callbacks for child nodes should be called on delete operations. |
|
Specifies whether SIL callbacks are invoked for false-when auto-deletion. |
|
Specifies whether SIL callbacks are invoked for defaults. |
|
Specifies if a missing SIL library file will be treated as an error or not. |
|
Specifies whether the SIL callbacks are invoked in reserved order for deletes or not. |
|
Force the YANG validation checks to be done before the SIL validate callbacks. |
|
Prevents the server from invoking the Global EDIT callback during the Validate Phase. |
|
Prevents the server from invoking the Global EDIT callback during the Apply Phase. |
|
Specifies that the server should skip the SIL edit callbacks during the load datastore initialization phase. |
|
Specifies the global default for evaluating when-stmts on operational data nodes during retrieval operations |
|
Controls whether SIL callbacks will be done for the candidate datastore |
|
Specifies that the server should output name of the module in which the data node is defined or not. |
|
Specifies the XML or JSON file to read which contains the configuration data needed to create desired mount-points. |
|
Specifies the Schema Mount Config file encoding. Based on this encoding the server will parse the config file accordingly. |
|
Specifies the IPv4 address to listen on when the socket-type parameter is set to 'tcp'. |
|
Specifies the TCP port number to listen on when the socket-type parameter is set to 'tcp'. |
|
Specifies which type of socket the server should create for incoming <ncx-connect> protocol sessions. |
|
Specifies the startup configuration file location to override the default. Not allowed if the --no-startup parameter is present. |
|
Specifies whether the server should stop, continue, or fallback to factory default if the startup configuration contains any recoverable errors (the bad configuration data can be removed)` |
|
Specifies the YANG configuration to use as the factory default config |
|
Specifies if unknown nodes can be pruned at boot-time from the startup config |
|
If true then skip the root check YANG validation when loading the startup configuration at boot time. |
|
If true, then sub-directories will be searched when looking for files. Otherwise just the specified directory will be used and none of its sub-directories (if any). |
|
The number of seconds to wait for a response from a sub-system before declaring a timeout. |
|
Specifies one or more user names to be given super user privileges. If ‘superuser’ is configured in your netconfd-pro.conf file, then that value will be overridden by your command line value. |
|
Specifies the YANG module(s) the server should use for system events such as a new session, configuration change, or capability change. |
|
Specifies default sort type for system ordered lists and leaf-lists |
|
Specifies whether system ordered lists and leaf-lists should be maintained in sorted order |
|
Specifies if the <candidate> or <running> configuration should be the edit target |
|
The number of seconds to wait for the TCP connect function to finish |
|
Automatically use a valid Subject Alternate Name as the username |
|
Specifies advanced OpenSSL cipher configuration settings. |
|
Specifies TLS Common Authentication should be used instead of Mutual Authentication. |
|
Specifies whether missing CRL Distribution Point is an error |
|
Specifies how Certificate Revocation List processing is done |
|
Enable extended NETCONF over TLS logging information |
|
Allow deprecated versions of TLS to be used |
|
Require TLS version 1.3 to be used for NETCONF over TLS sessions |
|
Specifies if leading and trailing XML whitespace should be trimmed |
|
Forces strict YANG XML ordering to be enforced |
|
Pass vendor-defined parameter string to instrumentation |
|
Prints the program version string and exits |
|
Block client sessions until <running> datastore is ready to use |
|
Treat all warnings as errors |
|
Controls how identifier lengths are checked |
|
Controls how line lengths are checked |
|
Suppresses the specified warning number |
|
Suppresses all YANG warnings |
|
Elevates the specified warning number to an error |
|
Specifies the sleep interval between ypwatcher program attempts to check availability of the server. |
|
Controls whether the server will support YANG-API/RESTCONF URL requests that contain a dash character '-' to indicate all instances of that key leaf. |
|
Enable or disable the IETF Call Home protocol |
|
Enable or disable automatic conversion to canonical data type format |
|
Enable or disable the :config-id capability URI |
|
Enable or disable the :confirmed-commit capability URI |
|
Enable or disable the DB-Config-Lock (system-wide edit lock) |
|
Enable or disable the <error-number> leaf in <error-info> data |
|
Enable or disable the IETF factory-default Support |
|
Enable or disable flushing data to disk when saving startup config |
|
Enable or disable the gNMI protocol |
|
Enable or disable the gRPC protocol |
|
Enable or disable allowing maintenance mode to be used |
|
Enable or disable module-tags feature |
|
Enable or disable the NETCONF over SSH protocol |
|
Enable or disable the NETCONF over TLS protocol |
|
Enable RFC 8639 Notifications even if 'bundle yang-push' not used |
|
Enable RFC 8525 YANG Library even if NMDA not used |
|
Enable or disable NMDA support |
|
Controls whether the server will support the :notification and :interleave capabilities or not. |
|
Controls whether OpenConfig pattern syntax will be checked |
|
Enable or disable the Regex Filter feature |
|
Enable or disable the RESTCONF protocol |
|
Enable or disable the :rollback-on-error NETCONF capability |
|
Enable or disable YANG Schema Mount support |
|
Enable or disable SNMP protocol support |
|
Enable or disable the <startup> database |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-support-save.yang YANG module |
|
Enable <term-msg> notification |
|
Enable or disable the :url capability |
|
Enable or disable FTP scheme in <url> parameter |
|
Enable or disable TFTP scheme in <url> parameter |
|
Enable or disable the :validate capability |
|
Enable or disable the error-severity field set to warning |
|
Enable or disable the YANG-API protocol |
|
Enable or disable the ietf-yang-library-augmentedby.yang YANG module |
|
Enable or disable the YANG/CBOR message encoding |
|
Enable or disable the ietf-yang-metadata.yang module |
|
Enable or disable YANG Patch if target=running |
|
Enable YANG Push 2 features |
|
Enable or disable strict YANG 1.1 <hello> message |
|
Enable the YP-COAP protocol |
|
Enable the YP-COAP over DTLS protocol |
|
Enable or disable the YP-SHELL protocol |
|
Enable or disable the yuma-system.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yuma-time-filter.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-callhome.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-cert-usermap.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-config-change.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-event-filter.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-event-stream.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-getbulk.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-ids.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-lock.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-sm-yanglib.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-system.yang module |
|
Enable or disable the yumaworks-templates.yang module |
|
Select the YANG/CBOR SID assignment mode |
|
The starting string for the server URL to use in Location header lines returned by YANG-API. The default is 'http://localhost'. |
|
IP address to use for YP-CoaP or YP-CoAP over DTLS protocols |
|
UDP port to use for YP-CoAP over DTLS protocol |
|
UDP port to use for YP-CoAP protocol |
|
Specifies the $YUMAPRO_HOME project root to use when searching for files |
Editing CLI Parameters at Run-Time
The yumaworks-server.yang module allows client sessions to alter the configuration parameters for the next reboot. This module should be enabled at the command line or in the configuration parameter file for the libyumaworks_server.so library to be loaded and this feature enabled. This module can also be loaded at run-time with the <load> operation.
netconfd-pro {
module yumaworks-server
}
If enabled, there will be a top-level configuration container named “server” that has all the CLI parameters as direct child nodes. Normal editing commands can be used to alter the parameter values.
> merge /server/max-sessions value=10
There are a small number of CLI parameters that can be edited at run-time and the new value will be activated immediately:
allowed-user
eventlog-size
hello-timeout:
idle-timeout
log-level
max-burst
max-cli-sessions: affects new sessions only
max-getbulk
max-sessions: affects new sessions only
subsys-timeout
The “server” configuration container is not saved in the normal YANG
configuration data (e.g., startup-cfg.xml). Instead, the CLI
configuration file (e.g., netconfd-pro.conf) will be updated when
the server restarts or shuts down. This will only be done if the
following conditions are met:
The --no-config CLI option was not used
The server has write permissions to rewrite the configuration file
If the server cannot save the CLI parameters upon restart or shutdown, then a warning log message will be generated. If the yumaworks-server.yang module is unloaded before the server exits then the CLI parameters will not be saved.
If the yumaworks-server module is loaded at runtime with the <load> operation, then the values set from the CLI parameters will be used to populate the /server container. This affects only the parameters that can be changed at run-time (listed above).
If the yumaworks-server module is unloaded at runtime with the <unload> operation, then the values set from the CLI parameters will be restored. This affects only the parameters that can be changed at run-time (listed above).
Using logrotate to Manage Log Files
The logrotate program on Linux can be used to archive log files automatically. This is typically done to manage the size of the log files.
The netconfd-pro supports logrotate using the USR2 signal. If this signal is sent to the server process, then the server will close and re-open its log file and audit-log file, if they are set. This will not be done if these logs are not being saved to file. Both files will be closed and re-opened, if present, even if the file was not rotated.
Logrotate config must be used with the "copytruncate" option and server should be started with --log-append parameter, this will not cause any data to be deleted from the log file.
There is a sample logrotate file located in the installed files. The following command can be used to copy it to the proper location.
> cp /usr/share/yumapro/util/netconfd-pro.logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/netconfd-pro
The standard log location (/var/log/netconfd-pro/) is used in this example logrotate configuration file. The parameter --fileloc-fhs should be set to 'true' to automatically use the standard FHS file locations.
The logrotate file shown is just an example. The lastaction/endscript directive is used to send the USR2 signal to the server, which causes the log files to be re-opened. Refer to the logrotate documentation for details on using this program.
/var/log/netconfd-pro/*.log {
size 1M
missingok
rotate 4
compress
delaycompress
copytruncate
notifempty
lastaction
/bin/kill -USR2 `cat /var/run/netconfd-pro/netconfd-pro.pid`
endscript
}
Maintenance Mode
If the --with-maintenance-mode parameter is set to 'true' (the default) then the server will allow the maintenance mode to be used. In maintenance mode, no client sessions can be started or used. Only YControl sessions can be used to allow server maintenance to occur without client session interference.
This mode cannot be set by clients. It can only be set through APIs in the server, either internally or through the DB-API service.
If maintenance mode is active, then the server will return an 'operation-failed' error-tag. The error-number will be '420' and the default error message is 'maintenance mode active'.
Disabling YumaWorks YANG Modules
There are several built-in YANG modules that the server normally loads without any extra configuration (E.g., ‘module parameter). The IETF standard modules cannot be disabled but the proprietary YumaWorks modules can be enabled or disabled with CLI parameters.
The following table describes the built-in modules that can be disabled:
Parameter |
Module |
Description |
|---|---|---|
any |
Hide the specified module from client discovery. Does not affect data returned to clients. |
|
<get-support-save> gathers support information. Must build source WITH_SUPPORT_SAVE=1 |
||
<term-msg> notification used to support yp-shell terminal diagnostic messages |
||
Yuma |
||
if-modified-since filter for <get> and <get-config> |
||
Run-time configuration or NETCONF Call Home connections. |
||
Configure NETCONF over TLS 'cert-to-name' mappings |
||
Add edit data to <netconf-config-change> Event notification (Security Risk!! Review YANG module before use!!) |
||
<event-filters> container to drop specific event types |
||
<event-streams> container to configure event streams and <clear-eventlog> RPC operation |
||
<get-bulk> operation to retrieve YANG list entries |
||
Contains transport identity values to add YControl and direct sessions to ietf-netconf-monitoring.yang <session> list |
||
<get-sm-yanglib> operation to retrieve Schema Mount YANG library |
||
Various operations and augments of <get> and <get-config> operations with additional filters. Dynamic module/bundle <load> and <unload> operations are included in this module. |
||
|
DB-Config-Lock Mode
The DB-Config-Lock mode allows the netconfd-pro to participate in a system-wide lock for modification of the <running> configuration datastore contents. Use of this system-wide lock require that the server is built using WITH_YCONTROL=1. The 'db_api.c' module contains APIs to allow the server and the “local” system to request and release the DB-Config-Lock.
The following CLI parameters affect DB-Config-Lock mode:
--with-db-lock=true required to use DB-Config-Lock.
--db-lock-retry-interval, --db-lock-timeout, and --subsys-timeout affect how long the server will wait for a DB-Config-Lock.
The DB-Config-Lock is described in the YANG module yumaworks-db-api.yang.
The following DB-API messages are used:
db-lock-init: Initialize the DB-Config-Lock service. The server will not allow any configuration modifications, including booting the startup configuration, until this message is properly handled by the server.
db-lock: The server sends this message to the DB-Config-Lock subsystem before the Apply/Commit/Rollback portion of an edit transaction to the <running> configuration, The validate phase callbacks are invoked without any DB-Config-Lock.
db-unlock: The server sends this event to a subsystem to release a DB-Config-Lock.
Configuration edits by all clients are affected by this lock.
Deferred Configuration Load Mode
It is possible in certain server configurations and deployments that the server will defer loading the running configuration at boot-time. Client sessions will be allowed but access to datastores is disabled.
If desired, all client protocol sessions (e.g., NETCONF, RESTCONF) can be blocked in this state.
Use the --wait-datastore-ready=true setting in the CLI parameters or parameter configuration file (e.g., netconfd-pro.conf).
Use the <get-ha-status> operation to retrieve some HA state information that might provide more details
The following corner-cases will cause the server to return “wrong config state” or “access-denied” errors while the server is waiting to be able to load the configuration:
YP-HA Standby Mode: the server is waiting to connect to the YP-HA Active Server
YP-HA Role Unknown: YP-HA is enabled but the YP-HA role is not known yet
SIL-SA Bundle Mode: the server has loaded 1 or more bundles that did not have SIL libraries found. This causes the server to wait for SIL-SA subsystems to register the missing bundles so all modules can be known
DB-Config-Lock Init Mode: The DB-Config-Lock mode is enabled but the DB-API subsystem providing this service has not registered or has terminated the Ycontrol session.